Utility of organotypic raphe slice cultures to investigate the effects of sustained exposure to selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitors on 5-HT release
- PMID: 20698856
- PMCID: PMC3010565
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00978.x
Utility of organotypic raphe slice cultures to investigate the effects of sustained exposure to selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitors on 5-HT release
Abstract
Background and purpose: Selective 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT, serotonin) reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are widely used antidepressants and their therapeutic effect requires several weeks of drug administration. The delayed onset of SSRI efficacy is due to the slow neuroadaptive changes of the 5-hydroxytryptaminergic (5-HTergic) system. In this study, we examined the acute and chronic effects of SSRIs on the 5-HTergic system using rat raphe slice cultures.
Experimental approach: For organotypic raphe slice cultures, mesencephalic coronal sections containing dorsal and median raphe nuclei were prepared from neonatal Wistar rats and cultured for 14-16 days.
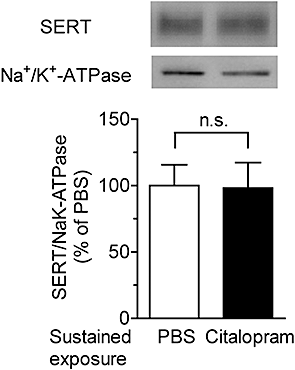
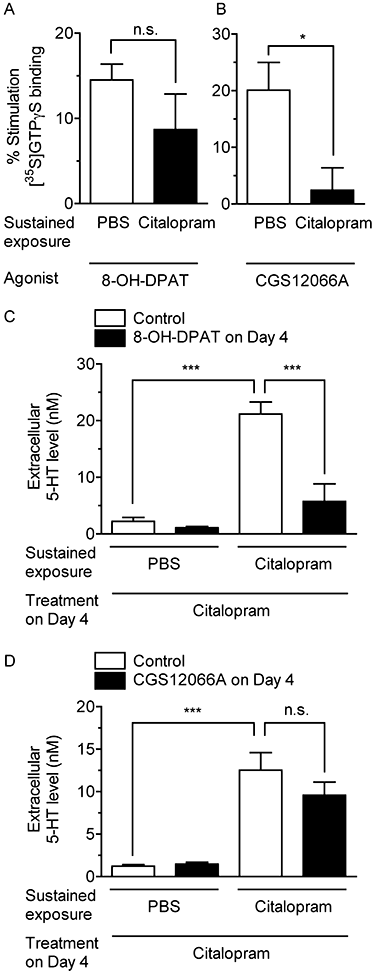
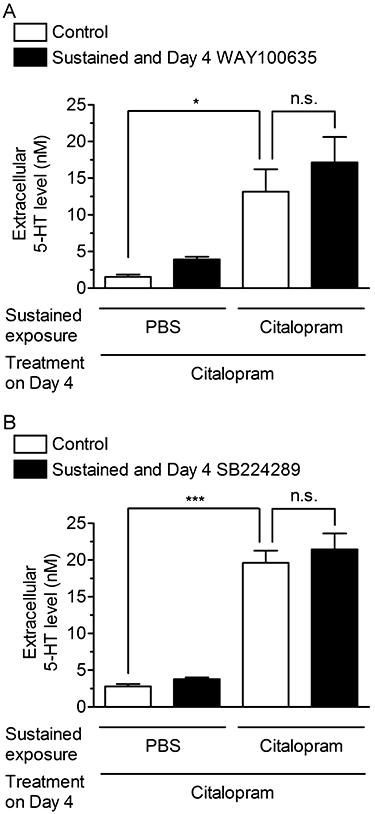
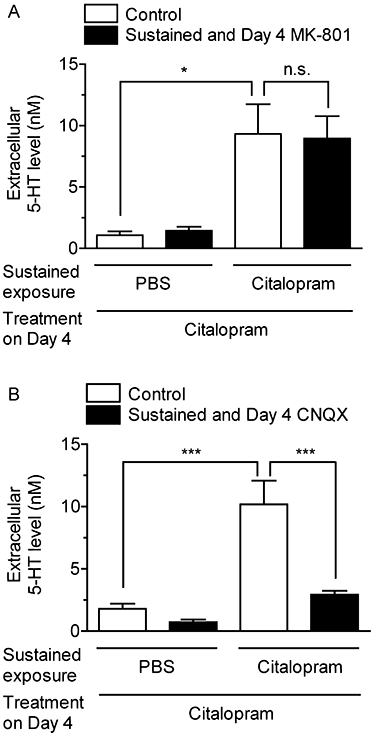
Key results: Acute treatment with citalopram, paroxetine or fluoxetine (0.1-10 µM) in the slice cultures slightly increased extracellular 5-HT levels, while sustained exposure for 4 days augmented the elevation of 5-HT level in a time-dependent manner. Sustained exposure to citalopram had no effect on tissue contents of 5-HT and its metabolite, expression of tryptophan hydroxylase or the membrane expression of 5-HT transporters. The augmented 5-HT release was attenuated by Ca(2+) -free incubation medium or treatment with tetrodotoxin. Experiments with 5-HT(1A/B) receptor agonists and antagonists revealed that desensitization of 5-HT(1) autoreceptors was not involved in the augmentation of 5-HT release. Finally, co-treatment with an α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)/kainate, but not an N-methyl-d-aspartate, receptor antagonist, suppressed this augmentation.
Conclusion and implications: These results suggest that sustained exposure to SSRIs induces the augmentation of exocytotic 5-HT release, which is caused, at least in part, by the activation of AMPA/kainate receptors in the raphe slice cultures.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chronic effects of antidepressants on serotonin release in rat raphe slice cultures: high potency of milnacipran in the augmentation of serotonin release.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 Nov;16(10):2295-306. doi: 10.1017/S1461145713000771. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23920436
-
Allosteric modulation of the effect of escitalopram, paroxetine and fluoxetine: in-vitro and in-vivo studies.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007 Feb;10(1):31-40. doi: 10.1017/S1461145705006462. Epub 2006 Feb 1. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007. PMID: 16448580
-
In vivo control of 5-hydroxytryptamine release by terminal autoreceptors in rat brain areas differentially innervated by the dorsal and median raphe nuclei.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998 Sep;358(3):315-22. doi: 10.1007/pl00005259. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9774218
-
[Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor(SSRI)].Nihon Rinsho. 2001 Aug;59(8):1519-22. Nihon Rinsho. 2001. PMID: 11519151 Review. Japanese.
-
Role of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in the mechanism of action of serotoninergic antidepressant drugs: recent findings from in vivo microdialysis studies.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1996;10(1):16-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1996.tb00145.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8900496 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the 5-HT4 receptor in chronic fluoxetine treatment-induced neurogenic activity and granule cell dematuration in the dentate gyrus.Mol Brain. 2015 May 15;8:29. doi: 10.1186/s13041-015-0120-3. Mol Brain. 2015. PMID: 25976618 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic antidepressant potentiates spontaneous activity of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons by decreasing GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of L-type calcium channels.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 19;7(1):13609. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13599-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29051549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abumaria N, Rygula R, Hiemke C, Fuchs E, Havemann-Reinecke U, Rüther E, et al. Effect of chronic citalopram on serotonin-related and stress-regulated genes in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007;17:417–429. - PubMed
-
- Alper RH, Nelson DL. Characterization of serotonin1A receptor-mediated [35S]GTPγS binding in rat hippocampal membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;343:303–312. - PubMed
-
- Bel N, Artigas F. Fluvoxamine preferentially increases extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in the raphe nuclei: an in vivo microdialysis study. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992;229:101–103. - PubMed
-
- Bel N, Artigas F. Chronic treatment with fluvoxamine increases extracellular serotonin in frontal cortex but not in raphe nuclei. Synapse. 1993;15:243–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

