Mutant FUS proteins that cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis incorporate into stress granules
- PMID: 20699327
- PMCID: PMC2981014
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq335
Mutant FUS proteins that cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis incorporate into stress granules
Abstract
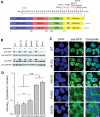
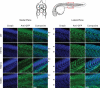
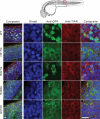
Mutations in the RNA-binding protein FUS (fused in sarcoma) are linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), but the mechanism by which these mutants cause motor neuron degeneration is not known. We report a novel ALS truncation mutant (R495X) that leads to a relatively severe ALS clinical phenotype compared with FUS missense mutations. Expression of R495X FUS, which abrogates a putative nuclear localization signal at the C-terminus of FUS, in HEK-293 cells and in the zebrafish spinal cord caused a striking cytoplasmic accumulation of the protein to a greater extent than that observed for recessive (H517Q) and dominant (R521G) missense mutants. Furthermore, in response to oxidative stress or heat shock conditions in cultures and in vivo, the ALS-linked FUS mutants, but not wild-type FUS, assembled into perinuclear stress granules in proportion to their cytoplasmic expression levels. These findings demonstrate a potential link between FUS mutations and cellular pathways involved in stress responses that may be relevant to altered motor neuron homeostasis in ALS.
Figures





References
-
- Dion P.A., Daoud H., Rouleau G.A. Genetics of motor neuron disorders: new insights into pathogenic mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009;10:769–782. doi:10.1038/nrg2680. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lemmens R., Moore M.J., Al-Chalabi A., Brown R.H., Jr, Robberecht W. RNA metabolism and the pathogenesis of motor neuron diseases. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:249–258. - PubMed
-
- van Blitterswijk M., Landers J.E. RNA processing pathways in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurogenetics. 2010;11:275–290. - PubMed
-
- Neumann M., Sampathu D.M., Kwong L.K., Truax A.C., Micsenyi M.C., Chou T.T., Bruce J., Schuck T., Grossman M., Clark C.M., et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314:130–133. doi:10.1126/science.1134108. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang I.F., Wu L.S., Shen C.K. TDP-43: an emerging new player in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2008;14:479–485. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2008.09.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

