Functional rescue of dystrophin-deficient mdx mice by a chimeric peptide-PMO
- PMID: 20700113
- PMCID: PMC2951563
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2010.151
Functional rescue of dystrophin-deficient mdx mice by a chimeric peptide-PMO
Erratum in
-
Functional Rescue of Dystrophin-Deficient mdx Mice by a Chimeric Peptide-PMO.Mol Ther. 2020 Oct 7;28(10):2297-2298. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.08.019. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32888402 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
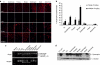
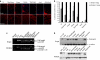
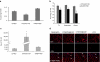
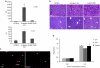
Splice modulation using antisense oligonucleotides (AOs) has been shown to yield targeted exon exclusion to restore the open reading frame and generate truncated but partially functional dystrophin protein. This has been successfully demonstrated in dystrophin-deficient mdx mice and in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) patients. However, DMD is a systemic disease; successful therapeutic exploitation of this approach will therefore depend on effective systemic delivery of AOs to all affected tissues. We have previously shown the potential of a muscle-specific/arginine-rich chimeric peptide-phosphorodiamidate morpholino (PMO) conjugate, but its long-term activity, optimized dosing regimen, capacity for functional correction and safety profile remain to be established. Here, we report the results of this chimeric peptide-PMO conjugate in the mdx mouse using low doses (3 and 6 mg/kg) administered via a 6 biweekly systemic intravenous injection protocol. We show 100% dystrophin-positive fibers and near complete correction of the dystrophin transcript defect in all peripheral muscle groups, with restoration of 50% dystrophin protein over 12 weeks, leading to correction of the DMD pathological phenotype and restoration of muscle function in the absence of detectable toxicity or immune response. Chimeric muscle-specific/cell-penetrating peptides therefore represent highly promising agents for systemic delivery of splice-correcting PMO oligomers for DMD therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Wood MJ, Gait MJ., and, Yin H. RNA-targeted splice-correction therapy for neuromuscular disease. Brain. 2010;133 Pt 4:957–972. - PubMed
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Janson AA, Kaman WE, Bremmer-Bout M, den Dunnen JT, Baas F, et al. Therapeutic antisense-induced exon skipping in cultured muscle cells from six different DMD patients. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:907–914. - PubMed
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Kaman WE, Weij R, den Dunnen JT, van Ommen GJ., and, van Deutekom JC. Exploring the frontiers of therapeutic exon skipping for Duchenne muscular dystrophy by double targeting within one or multiple exons. Mol Ther. 2006;14:401–407. - PubMed
-
- Alter J, Lou F, Rabinowitz A, Yin H, Rosenfeld J, Wilton SD, et al. Systemic delivery of morpholino oligonucleotide restores dystrophin expression bodywide and improves dystrophic pathology. Nat Med. 2006;12:175–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

