hI-con1, a factor VII-IgGFc chimeric protein targeting tissue factor for immunotherapy of uterine serous papillary carcinoma
- PMID: 20700124
- PMCID: PMC2966612
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605760
hI-con1, a factor VII-IgGFc chimeric protein targeting tissue factor for immunotherapy of uterine serous papillary carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Uterine serous papillary adenocarcinoma (USPC) is a highly aggressive variant of endometrial cancer. Human immuno-conjugate molecule (hI-con1) is an antibody-like molecule targeted against tissue factor (TF), composed of two human Factor VII (fVII) as the targeting domain, fused to human immunoglobulin (Ig) G1 Fc as an effector domain. We evaluated hI-con1 potential activity against primary chemotherapy-resistant USPC cell lines expressing different levels of TF.
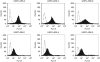
Methods: A total of 16 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded USPC samples were evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) for TF expression. Six primary USPC cell lines, half of which overexpress the epidermal growth factor type II (HER2/neu) receptor at 3+ levels, were assessed by flow cytometry and real-time PCR for TF expression. Sensitivity to hI-con1-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (IDCC) was evaluated in 5-hour-chromium release assays. Finally, to investigate the effect of interleukin-2 (IL-2) on IDCC, 5-h (51)Cr assays were also conducted in the presence of low doses of IL-2 (i.e., 50-100 IU ml(-1)).
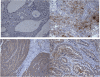
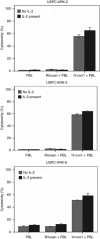
Results: Cytoplasmic and/or membrane TF expression was observed in all 16 (100%) USPC samples tested by IHC, but not in normal endometrium. High expression of TF was found in 50% (three out of six) of the USPC cell lines tested by real-time PCR and flow cytometry when compared with normal endometrial cells (NECs; P<0.001). Uterine serous papillary adenocarcinoma cell lines overexpressing TF, regardless of their high or low HER2/neu expression, were highly sensitive to IDCC (mean killing+/-s.d., 65.6+/-3.7%, range 57.5-77.0%, P<0.001), although negligible cytotoxicity against USPC was seen in the absence of hI-con1 or in the presence of Rituximab control antibody. The addition of low doses of IL-2 further increased the cytotoxic effect induced by hI-con1 against chemotherapy-resistant USPC.
Conclusion: hI-con1 induces strong cytotoxicity against primary chemotherapy-resistant USPC cell lines overexpressing TF. The hI-con1 may represent a novel therapeutic agent for the treatment of patients harbouring advanced, recurrent and/or metastatic USPC refractory to standard treatment modalities.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of tissue factor in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix: implications for immunotherapy with hI-con1, a factor VII-IgGFc chimeric protein targeting tissue factor.BMC Cancer. 2011 Jun 22;11:263. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-263. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21693061 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue factor expression in ovarian cancer: implications for immunotherapy with hI-con1, a factor VII-IgGF(c) chimeric protein targeting tissue factor.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2011 Oct;28(7):689-700. doi: 10.1007/s10585-011-9401-0. Epub 2011 Jul 2. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2011. PMID: 21725665 Free PMC article.
-
Uterine serous papillary carcinomas overexpress human trophoblast-cell-surface marker (Trop-2) and are highly sensitive to immunotherapy with hRS7, a humanized anti-Trop-2 monoclonal antibody.Cancer. 2011 Jul 15;117(14):3163-72. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25891. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21246534 Free PMC article.
-
The management of serous papillary uterine cancer.Curr Opin Oncol. 2006 Sep;18(5):494-9. doi: 10.1097/01.cco.0000239890.36408.75. Curr Opin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16894299 Review.
-
Is uterine serous papillary carcinoma a BRCA1-related disease? Case report and review of the literature.Gynecol Oncol. 1999 Nov;75(2):300-4. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1999.5568. Gynecol Oncol. 1999. PMID: 10525392 Review.
Cited by
-
Micro- and Macronutrients in Endometrial Cancer-From Metallomic Analysis to Improvements in Treatment Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 14;25(18):9918. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189918. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effective treatment of chemoresistant breast cancer in vitro and in vivo by a factor VII-targeted photodynamic therapy.Br J Cancer. 2011 Apr 26;104(9):1401-9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.88. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Br J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21427724 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells are crucial for the efficacy of Icon (factor VII/human IgG1 Fc) immunotherapy in human tongue cancer.BMC Immunol. 2010 Oct 12;11:49. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-49. BMC Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20939894 Free PMC article.
-
The roles and clinical applications of interleukins in endometrial carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 30;12:1001693. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1001693. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Antibody-Like Immunoconjugates against Tissue Factor with the Potential to Treat Angiogenesis-Dependent as Well as Macrophage-Associated Human Diseases.Antibodies (Basel). 2018 Mar;7(1):8. doi: 10.3390/antib7010008. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Antibodies (Basel). 2018. PMID: 31105982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abulafia O, Triest WE, Sherer DM (1999) Angiogenesis in malignancies of the female genital tract. Gynecol Oncol 72: 220–231 - PubMed
-
- Alessi P, Ebbinghaus C, Neri D (2004) Molecular targeting of angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 4(1654): 39–49 - PubMed
-
- Bohkman JV (1983) Two pathogenetic types of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 15: 10–17 - PubMed
-
- Bristow RE (1999) Endometrial cancer. Curr Opin Oncol 11: 388–393 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

