Characterization and functional expression of the natriuretic peptide system in human lens epithelial cells
- PMID: 20700369
- PMCID: PMC2852620
Characterization and functional expression of the natriuretic peptide system in human lens epithelial cells
Abstract
Purpose: The family of natriuretic peptides (NPs); atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), and C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) as well as three associated receptors (NPRs); natriuretic peptide receptor A (NPR-A), natriuretic peptide receptor B (NPR-B), and natriuretic peptide receptor C (NPR-C) has never been documented in human lens epithelial cells. The study described herein was designed to demonstrate both expression and functionality of components of the natriuretic peptides and natriuretic peptide receptors in the human lens epithelial cell line, HLE-B3 and in normal human lens epithelial cell cultures (nHLE).
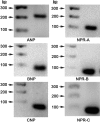
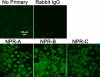
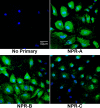
Methods: Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) along with confirmation by DNA sequencing and real-time quantitative RT-PCR was used to identify and demonstrate expression of mRNA for the natriuretic peptide family. Authentication of protein expression of the natriuretic peptide receptors was determined by using formaldehyde-fixed, Saponin-permeabilized cells (HLE-B3) or methanol:acetone-fixed and permeabilized cells (nHLE) using conventional immunofluorescence techniques. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to determine cyclic GMP (cGMP) activity as stimulated by exogenous addition of natriuretic peptides.
Results: Using RT-PCR with confirmation by DNA sequencing and real-time quantitative RT-PCR, HLE-B3 cells were shown to express mRNA for ANP, BNP, and CNP along with their associated receptors. Conventional immunofluorescence on the permeabilized cells confirmed positive diffuse staining indicating the presence of the three natriuretic peptide receptors in both HLE-B3 and nHLE cells. All three natriuretic peptides educe a cGMP response in the rank order CNP>>ANP approximately BNP indicating that the natriuretic peptide family is functional in HLE-B3 cells.
Conclusions: The data indicates that ANP, BNP, and CNP and natriuretic peptide receptor transcripts are expressed and are functional in human lens epithelial cells. The cellular expression of NPs and NPRs, as well as the demonstration that all three NPs activate guanylyl cyclase suggests a potential role in maintaining lens epithelial cell homeostasis.
Figures
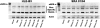
References
-
- Koller KJ, Goeddel DV. Molecular Biology of the Natriuretic Peptides and their Receptors. Circulation. 1992;86:1081–8. - PubMed
-
- Murthy KS, Teng BQ, Zhou H, Jin JG, Grider JR, Makhlouf GMG. (i-1)/G(i-2)-dependent signaling by single-transmembrane natriuretic peptide clearance receptor. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;278:G974–80. - PubMed
-
- Woodard GE, Rosado JA. Natriuretic peptides in vascular physiology and pathology. Int Rev Cell Mol Bio. 2008;268:59–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
