Multiple independent loci at chromosome 15q25.1 affect smoking quantity: a meta-analysis and comparison with lung cancer and COPD
- PMID: 20700436
- PMCID: PMC2916847
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001053
Multiple independent loci at chromosome 15q25.1 affect smoking quantity: a meta-analysis and comparison with lung cancer and COPD
Abstract
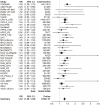
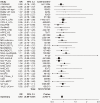
Recently, genetic association findings for nicotine dependence, smoking behavior, and smoking-related diseases converged to implicate the chromosome 15q25.1 region, which includes the CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 cholinergic nicotinic receptor subunit genes. In particular, association with the nonsynonymous CHRNA5 SNP rs16969968 and correlates has been replicated in several independent studies. Extensive genotyping of this region has suggested additional statistically distinct signals for nicotine dependence, tagged by rs578776 and rs588765. One goal of the Consortium for the Genetic Analysis of Smoking Phenotypes (CGASP) is to elucidate the associations among these markers and dichotomous smoking quantity (heavy versus light smoking), lung cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). We performed a meta-analysis across 34 datasets of European-ancestry subjects, including 38,617 smokers who were assessed for cigarettes-per-day, 7,700 lung cancer cases and 5,914 lung-cancer-free controls (all smokers), and 2,614 COPD cases and 3,568 COPD-free controls (all smokers). We demonstrate statistically independent associations of rs16969968 and rs588765 with smoking (mutually adjusted p-values<10(-35) and <10(-8) respectively). Because the risk alleles at these loci are negatively correlated, their association with smoking is stronger in the joint model than when each SNP is analyzed alone. Rs578776 also demonstrates association with smoking after adjustment for rs16969968 (p<10(-6)). In models adjusting for cigarettes-per-day, we confirm the association between rs16969968 and lung cancer (p<10(-20)) and observe a nominally significant association with COPD (p = 0.01); the other loci are not significantly associated with either lung cancer or COPD after adjusting for rs16969968. This study provides strong evidence that multiple statistically distinct loci in this region affect smoking behavior. This study is also the first report of association between rs588765 (and correlates) and smoking that achieves genome-wide significance; these SNPs have previously been associated with mRNA levels of CHRNA5 in brain and lung tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
NLS is the spouse of S.F. Saccone, who is listed as an inventor on a patent, “Markers of Addiction”, covering the use of certain SNPs in diagnosing, prognosing, and treating addiction. LJB, JCW and JPR are listed as inventors on a patent, “Markers of Addiction,” covering the use of certain SNPs in diagnosing, prognosing, and treating addiction. LJB has served as a consultant to Pfizer in 2008. XK is a full time employee of GlaxoSmithKline. SP was a full time employee of GlaxoSmithKline. Current affiliation is with Hoffman-La Roche. JK has served as a consultant to Pfizer in 2008. MDL has served as a consultant to NIH, deCODE genetics, University of Pennsylvania, Reckitt Benckiser Pharmaceuticals, Pennsylvania Department of Health, and Informational Managements Consulting. Dr. Li also serves as a scientific advisor to ADial Pharmaceuticals. TJP receives compensation from the University of Mississippi Medical Center; part of his salary has been supported by grants from NIDA, NCI, the University of Mississippi Health Care Cancer Institute, the Mississippi State Department of Health, Pfizer Inc., and GlaxoSmithKline.
Figures

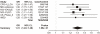

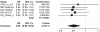

References
-
- Mackay J, Eriksen M, Shafey O, editors. The Tobacco Atlas. 2 ed. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2006.
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 CN025516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K01DA019498/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA019498/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CA55769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25513/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087895/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD031921/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA060691/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25511/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA13321/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 AA017688/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA-12844/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025512/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD041020/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA60691/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA133996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12890/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA024758/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG04422-01/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA017889/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25514/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 ES011080/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011998/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL072903/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25512/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025511/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA026901/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA021913/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CA127219/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK070756/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025522/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025513/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA127219/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA13320/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025524/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025476/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007464/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- CA121197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA012854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AA015336/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 5P01DK070756/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004424/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25515/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA026911/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN075022/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD31921/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013321/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30ES007784/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA027070/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN-25524/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA87895/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA055769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004422/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG04424/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- CA133996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA12854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K25 GM69590/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025518/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012844/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011949/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012845/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA022453/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA11998/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007784/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25404/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25516/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DA019951/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025515/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA021237/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA-13783/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K25 GM069590/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL035464/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01-CN-25476/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC35145/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DA023166/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL72903/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DA12849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21DA027070/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013783/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC035145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN-75022/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA22453/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12854/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25518/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025514/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AA11330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013320/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DA011015/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25522/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K01DA024758/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL035464/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

