From open radical hysterectomy to robot-assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy for early stage cervical cancer: aspects of a single institution learning curve
- PMID: 20700514
- PMCID: PMC2914863
- DOI: 10.1007/s10397-010-0572-5
From open radical hysterectomy to robot-assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy for early stage cervical cancer: aspects of a single institution learning curve
Abstract
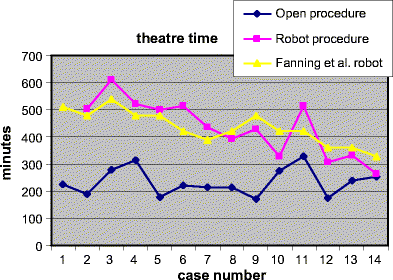
We analysed the introduction of the robot-assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy in patients with early-stage cervical cancer with respect to patient benefits and surgeon-related aspects of a surgical learning curve. A retrospective review of the first 14 robot-assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomies and the last 14 open radical hysterectomies in a similar clinical setting with the same surgical team was conducted. Patients were candidates for a laparoscopic sentinel node procedure, pelvic lymph node dissection and open radical hysterectomy (RH) before August 2006 and were candidates for a laparoscopic sentinel node procedure, pelvic lymph node dissection and robot-assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (RALRH) after August 2006. Overall, blood loss in the open cases was significantly more compared with the robot cases. Median hospital stay after RALRH was 5 days less than after RH. The median theatre time in the learning period for the robot procedure was reduced from 9 h to less that 4 h and compared well to the 3 h and 45 min for an open procedure. Three complications occurred in the open group and one in the robot group. RALRH is feasible and of benefit to the patient with early stage cervical cancer by a reduction of blood loss and reduced hospital stay. Introduction of this new technique requires a learning curve of less than 15 cases that will reduce the operating time to a level comparable to open surgery.
Figures

References
-
- Wertheim E (1912) The extended abdominal operation for carcinoma uteri. Am J Obstet Gynecol 169–232
-
- Meigs J. The Wertheim operation for carcinoma of the cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1945;40:542–543.
-
- Canis M, Mage G, Wattiez A, Pouly JL, Manhes H, Bruhat MA. Does endoscopic surgery have a role in radical surgery of cancer of the cervix uteri? J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1990;19(7):921. - PubMed
-
- Nezhat CR, Burrell MO, Nezhat FR, Benigno BB, Welander CE. Laparoscopic radical hysterectomy with paraaortic and pelvic node dissection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166(3):864–865. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
