Genome wide screen identifies microsatellite markers associated with acute adverse effects following radiotherapy in cancer patients
- PMID: 20701746
- PMCID: PMC2928773
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-123
Genome wide screen identifies microsatellite markers associated with acute adverse effects following radiotherapy in cancer patients
Abstract
Background: The response of normal tissues in cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy varies, possibly due to genetic differences underlying variation in radiosensitivity.
Methods: Cancer patients (n = 360) were selected retrospectively from the RadGenomics project. Adverse effects within 3 months of radiotherapy completion were graded using the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria; high grade group were grade 3 or more (n = 180), low grade group were grade 1 or less (n = 180). Pooled genomic DNA (gDNA) (n = 90 from each group) was screened using 23,244 microsatellites. Markers with different inter-group frequencies (Fisher exact test P < 0.05) were analyzed using the remaining pooled gDNA. Silencing RNA treatment was performed in cultured normal human skin fibroblasts.
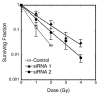
Results: Forty-seven markers had positive association values; including one in the SEMA3A promoter region (P = 1.24 x 10(-5)). SEMA3A knockdown enhanced radiation resistance.
Conclusions: This study identified 47 putative radiosensitivity markers, and suggested a role for SEMA3A in radiosensitivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chromosomal in-vitro radiosensitivity of lymphocytes in radiotherapy patients and AT-homozygotes.Strahlenther Onkol. 1998 Oct;174(10):510-6. doi: 10.1007/BF03038983. Strahlenther Onkol. 1998. PMID: 9810318
-
Microsatellite polymorphisms in DNA repair genes XRCC1, XRCC3 and XRCC5 in patients with gynecological tumors: association with late clinical radiosensitivity and cancer incidence.Radiat Res. 2005 Sep;164(3):237-44. doi: 10.1667/rr3417.1. Radiat Res. 2005. PMID: 16137195 Clinical Trial.
-
Rare microsatellite polymorphisms in the DNA repair genes XRCC1, XRCC3 and XRCC5 associated with cancer in patients of varying radiosensitivity.Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1997 Jul;23(4):237-47. doi: 10.1007/BF02674415. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1997. PMID: 9542526
-
Biomarkers of radiation exposure: can they predict normal tissue radiosensitivity?Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2013 Oct;25(10):610-6. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2013.06.010. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2013. PMID: 23870757 Review.
-
Does variability in normal tissue reactions after radiotherapy have a genetic basis--where and how to look for it?Radiother Oncol. 2002 Aug;64(2):131-40. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(02)00154-8. Radiother Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12242122 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiogenomics: using genetics to identify cancer patients at risk for development of adverse effects following radiotherapy.Cancer Discov. 2014 Feb;4(2):155-65. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0197. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Cancer Discov. 2014. PMID: 24441285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological complexities in radiation carcinogenesis and cancer radiotherapy: impact of new biological paradigms.Genes (Basel). 2012 Jan 20;3(1):90-114. doi: 10.3390/genes3010090. Genes (Basel). 2012. PMID: 24704845 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics and genomics of radiotherapy toxicity: towards prediction.Genome Med. 2011 Aug 23;3(8):52. doi: 10.1186/gm268. Genome Med. 2011. PMID: 21861849 Free PMC article.
-
Common variants in the COL4A4 gene confer susceptibility to lattice degeneration of the retina.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039300. Epub 2012 Jun 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22723992 Free PMC article.
-
Class-3 Semaphorins and Their Receptors: Potent Multifunctional Modulators of Tumor Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 28;20(3):556. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030556. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30696103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Iwakawa M, Noda S, Yamada S, Yamamoto N, Miyazawa Y, Yamazaki H, Kawakami Y, Matsui Y, Tsujii H, Mizoe J, Oda E, Fukunaga Y, Imai T. Analysis of non-genetic risk factors for adverse skin reactions to radiotherapy among 284 breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer. 2006;13:300–307. doi: 10.2325/jbcs.13.300. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

