Genome wide screen identifies microsatellite markers associated with acute adverse effects following radiotherapy in cancer patients
- PMID: 20701746
- PMCID: PMC2928773
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-123
Genome wide screen identifies microsatellite markers associated with acute adverse effects following radiotherapy in cancer patients
Abstract
Background: The response of normal tissues in cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy varies, possibly due to genetic differences underlying variation in radiosensitivity.
Methods: Cancer patients (n = 360) were selected retrospectively from the RadGenomics project. Adverse effects within 3 months of radiotherapy completion were graded using the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria; high grade group were grade 3 or more (n = 180), low grade group were grade 1 or less (n = 180). Pooled genomic DNA (gDNA) (n = 90 from each group) was screened using 23,244 microsatellites. Markers with different inter-group frequencies (Fisher exact test P < 0.05) were analyzed using the remaining pooled gDNA. Silencing RNA treatment was performed in cultured normal human skin fibroblasts.
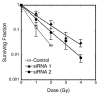
Results: Forty-seven markers had positive association values; including one in the SEMA3A promoter region (P = 1.24 x 10(-5)). SEMA3A knockdown enhanced radiation resistance.
Conclusions: This study identified 47 putative radiosensitivity markers, and suggested a role for SEMA3A in radiosensitivity.
Figures
References
-
- Iwakawa M, Noda S, Yamada S, Yamamoto N, Miyazawa Y, Yamazaki H, Kawakami Y, Matsui Y, Tsujii H, Mizoe J, Oda E, Fukunaga Y, Imai T. Analysis of non-genetic risk factors for adverse skin reactions to radiotherapy among 284 breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer. 2006;13:300–307. doi: 10.2325/jbcs.13.300. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

