HMGA1 down-regulation is crucial for chromatin composition and a gene expression profile permitting myogenic differentiation
- PMID: 20701767
- PMCID: PMC2928187
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-11-64
HMGA1 down-regulation is crucial for chromatin composition and a gene expression profile permitting myogenic differentiation
Abstract
Background: High mobility group A (HMGA) proteins regulate gene transcription through architectural modulation of chromatin and the formation of multi-protein complexes on promoter/enhancer regions. Differential expression of HMGA variants has been found to be important for distinct differentiation processes and deregulated expression was linked to several disorders. Here we used mouse C2C12 myoblasts and C2C12 cells stably over-expressing HMGA1a-eGFP to study the impact of deregulated HMGA1 expression levels on cellular differentiation.
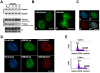
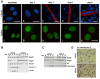
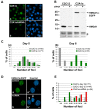
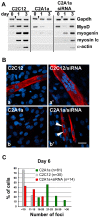
Results: We found that induction of the myogenic or osteogenic program of C2C12 cells caused an immediate down-regulation of HMGA1. In contrast to wild type C2C12 cells, an engineered cell line with stable over-expression of HMGA1a-eGFP failed to differentiate into myotubes. Immunolocalization studies demonstrated that sustained HMGA1a-eGFP expression prevented myotube formation and chromatin reorganization that normally accompanies differentiation. Western Blot analyses showed that elevated HMGA1a-eGFP levels affected chromatin composition through either down-regulation of histone H1 or premature expression of MeCP2. RT-PCR analyses further revealed that sustained HMGA1a expression also affected myogenic gene expression and caused either down-regulation of genes such as MyoD, myogenin, Igf1, Igf2, Igfbp1-3 or up-regulation of the transcriptional repressor Msx1. Interestingly, siRNA experiments demonstrated that knock-down of HMGA1a was required and sufficient to reactivate the myogenic program in induced HMGA1a over-expressing cells.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that HMGA1 down-regulation after induction is required to initiate the myogenic program in C2C12 cells. Sustained HMGA1a expression after induction prevents expression of key myogenic factors. This may be due to specific gene regulation and/or global effects on chromatin. Our data further corroborate that altered HMGA1 levels influence the expression of other chromatin proteins. Thus, HMGA1 is able to establish a specific chromatin composition. This work contributes to the understanding of how differential HMGA1 expression is involved in chromatin organization during cellular differentiation processes and it may help to comprehend effects of HMGA1 over-expression occurring in malign or benign tumours.
Figures
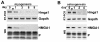

References
-
- Catez F, Hock R. Binding and interplay of HMG proteins on chromatin: Lessons from live cell imaging. Biochim Biophys acta. 2010;1799:15–27. - PubMed
-
- Reeves R, Beckerbauer L. HMGI/Y proteins: flexible regulators of transcription and chromatin structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1519:13–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

