Dopamine reveals neural circuit mechanisms of fly memory
- PMID: 20701984
- PMCID: PMC2947577
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.07.001
Dopamine reveals neural circuit mechanisms of fly memory
Abstract
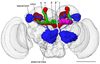
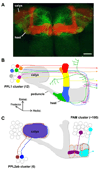
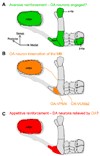
A goal of memory research is to understand how changing the weight of specific synapses in neural circuits in the brain leads to an appropriate learned behavioral response. Finding the relevant synapses should allow investigators to probe the underlying physiological and molecular operations that encode memories and permit their retrieval. In this review I discuss recent work in Drosophila that implicates specific subsets of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in aversive reinforcement and appetitive motivation. The zonal architecture of these DA neurons is likely to reveal the functional organization of aversive and appetitive memory in the mushroom bodies. Combinations of fly DA neurons might code negative and positive value, consistent with a motivational systems role as proposed in mammals.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Joshua M, et al. The dynamics of dopamine in control of motor behavior. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2009;19:615–620. - PubMed
-
- Dayan P, Balleine BW. Reward, motivation, and reinforcement learning. Neuron. 2002;36:285–298. - PubMed
-
- Wise RA. Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:483–494. - PubMed
-
- Montague PR, et al. Computational roles for dopamine in behavioural control. Nature. 2004;431:760–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

