Foxm1 transcription factor is required for maintenance of pluripotency of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells
- PMID: 20702419
- PMCID: PMC3001083
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq715
Foxm1 transcription factor is required for maintenance of pluripotency of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells
Abstract
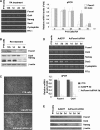
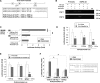
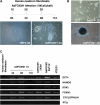
Transcription factor Foxm1 plays a critical role during embryonic development and its expression is repressed during retinoic acid (RA)-induced differentiation of pluripotent P19 embryonal carcinoma cells at the early stage, correlated with downregulation of expression of pluripotency markers. To study whether Foxm1 participates in the maintenance of pluripotency of stem cells, we knock down Foxm1 expression in P19 cells and identify that Oct4 are regulated directly by Foxm1. Knockdown of Foxm1 also results in spontaneous differentiation of P19 cells to mesodermal derivatives, such as muscle and adipose tissues. Maintaining Foxm1 expression prevents the downregulation of pluripotency-related transcription factors such as Oct4 and Nanog during P19 cell differentiation. Furthermore, overexpression of FOXM1 alone in RA-differentiated P19 cells (4 days) or human newborn fibroblasts restarts the expression of pluripotent genes Oct4, Nanog and Sox2. Together, our results suggest a critical involvement of Foxm1 in maintenance of stem cell pluripotency.
Figures


References
-
- Martin G. Teratocarcinomas and mammalian embryogenesis. Science. 1980;209:768–776. - PubMed
-
- McBurney MW, Rogers BJ. Isolation of male embryonal carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev. Biol. 1982;89:503–508. - PubMed
-
- Rossant J, McBurney MW. The developmental potential of a euploid male teratocarcinoma cell line after blastocyst injection. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1982;70:99–112. - PubMed
-
- McBurney MW, Jones-Villeneuve EM, Edwards MK, Anderson PJ. Control of muscle and neuronal differentiation in a cultured embryonal carcinoma cell line. Nature. 1982;299:165–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

