Life-course analysis of a fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) gene variant and body mass index in the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966 using structural equation modeling
- PMID: 20702506
- PMCID: PMC2938267
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwq178
Life-course analysis of a fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) gene variant and body mass index in the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966 using structural equation modeling
Abstract
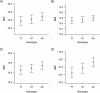
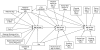
The association between variation in the fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) gene and adulthood body mass index (BMI; weight (kg)/height (m)(2)) is well-replicated. More thorough analyses utilizing phenotypic data over the life course may deepen our understanding of the development of BMI and thus help in the prevention of obesity. The authors used a structural equation modeling approach to explore the network of variables associated with BMI from the prenatal period to age 31 years (1965-1997) in 4,435 subjects from the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1966. The use of structural equation modeling permitted the easy inclusion of variables with missing values in the analyses without separate imputation steps, as well as differentiation between direct and indirect effects. There was an association between the FTO single nucleotide polymorphism rs9939609 and BMI at age 31 years that persisted after controlling for several relevant factors during the life course. The total effect of the FTO variant on adult BMI was mostly composed of the direct effect, but a notable part was also arising indirectly via its effects on earlier BMI development. In addition to well-established genetic determinants, many life-course factors such as physical activity, in spite of not showing mediation or interaction, had a strong independent effect on BMI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) rs9939609 polymorphism modifies the relationship between body mass index and affective symptoms through the life course: a prospective birth cohort study.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Mar 13;8(1):62. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0110-1. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29531329 Free PMC article.
-
The common rs9939609 variant of the fat mass and obesity-associated gene is associated with obesity risk in children and adolescents of Beijing, China.BMC Med Genet. 2010 Jul 5;11:107. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-107. BMC Med Genet. 2010. PMID: 20598163 Free PMC article.
-
The common variant in the FTO gene did not modify the effect of lifestyle changes on body weight: the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009 Apr;17(4):832-6. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.618. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009. PMID: 19180072 Clinical Trial.
-
Education modulates the association of the FTO rs9939609 polymorphism with body mass index and obesity risk in the Mediterranean population.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2012 Aug;22(8):651-8. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2010.10.006. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 21186106 Free PMC article.
-
The common FTO variant rs9939609 is not associated with BMI in a longitudinal study on a cohort of Swedish men born 1920-1924.BMC Med Genet. 2009 Dec 9;10:131. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-10-131. BMC Med Genet. 2009. PMID: 20003232 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetics of Obesity: What have we Learned?Curr Genomics. 2011 May;12(3):169-79. doi: 10.2174/138920211795677895. Curr Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22043165 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of gene-environment interactions in human obesity.Clin Sci (Lond). 2016 Sep 1;130(18):1571-97. doi: 10.1042/CS20160221. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016. PMID: 27503943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Body mass index and overweight in relation to residence distance and population density: experience from the Northern Finland birth cohort 1966.BMC Public Health. 2013 Oct 8;13:938. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-938. BMC Public Health. 2013. PMID: 24103455 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the fourth wave of genome-wide obesity association studies.Nutr Diabetes. 2012 Jul 30;2(7):e37. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2012.9. Nutr Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 23168490 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective analysis of the association of a common variant of FTO (rs9939609) with adiposity in children: results of the IDEFICS study.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048876. Epub 2012 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23155422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith SC., Jr Multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 2007;120(3 suppl 1):S3–S11. - PubMed
-
- Thorleifsson G, Walters GB, Gudbjartsson DF, et al. Genome-wide association yields new sequence variants at seven loci that associate with measures of obesity. Nat Genet. 2009;41(1):18–24. - PubMed
-
- Meyre D, Delplanque J, Chèvre JC, et al. Genome-wide association study for early-onset and morbid adult obesity identifies three new risk loci in European populations. Nat Genet. 2009;41(2):157–159. - PubMed

