Endogenous activation of glucokinase by 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase is glucose dependent
- PMID: 20702580
- PMCID: PMC5417398
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2010-0115
Endogenous activation of glucokinase by 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase is glucose dependent
Abstract
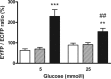
Glucokinase (GK) plays a crucial role as glucose sensor in glucose-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells. The bifunctional enzyme 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFK-2/FBPase-2) acts as an endogenous GK activator. Therefore, the goal of this study was the analysis of GK-PFK-2/FBPase-2 complex formation and its effect on metabolic stimulus-secretion coupling in β-cells in dependence upon glucose. The interaction between GK and PFK-2/FBPase-2 was analyzed in insulin-secreting MIN6 cells with a new fluorescence-based mammalian two-hybrid system. In contrast to the commonly used mammalian two-hybrid systems that require sampling before detection, the system used allows monitoring of the effects of environmental changes on protein-protein interactions on the single-cell level. Increasing the glucose concentration in the cell culture medium from 3 to 10 and 25 mmol/liter amplified the interaction between the enzymes stepwise. Importantly, in line with these results, overexpression of PFK-2/FBPase-2 in MIN6 cells evoked only at 10 and 25 mmol/liter, an increase in insulin secretion. Furthermore, a PFK-2/FBPase-2 mutant with an abolished GK-binding motif neither showed a glucose-dependent GK binding nor was able to increase insulin secretion. The results obtained with the mammalian two-hybrid system could be confirmed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer experiments in COS cells. Furthermore, the established interaction between GK and the liver GRP served in all experiments as a control. Thus, this study clearly showed that binding and activation of GK by PFK-2/FBPase-2 in β-cells is promoted by glucose, resulting in an enhancement of insulin secretion at stimulatory glucose concentrations, without affecting basal insulin secretion.
Figures





References
-
- Baltrusch S, Tiedge M2006. Glucokinase regulatory network in pancreatic β-cells and liver. Diabetes 55(Suppl 2):S55–S64
-
- Lenzen S, Panten U1988. Signal recognition by pancreatic B-cells. Biochem Pharmacol 37:371–378 - PubMed
-
- Meglasson MD, Matschinsky FM1984. New perspectives on pancreatic islet glucokinase. Am J Physiol 246:E1–E13 - PubMed
-
- Matschinsky FM1996. Banting Lecture 1995. A lesson in metabolic regulation inspired by the glucokinase glucose sensor paradigm. Diabetes 45:223–241 - PubMed

