Induction of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-responsive genes and modulation of the immunoglobulin M response by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in primary human B cells
- PMID: 20702590
- PMCID: PMC2955211
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq234
Induction of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-responsive genes and modulation of the immunoglobulin M response by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in primary human B cells
Abstract
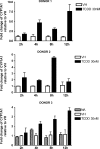
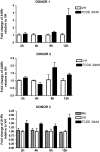
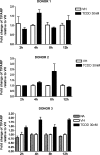
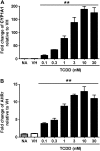
Past studies in rodent models identified the suppression of primary humoral immune responses as one of the most sensitive sequela associated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) exposure. Yet, the sensitivity of humoral immunity to TCDD in humans represents an important toxicological data gap. Therefore, the objectives of this investigation were two-fold. The first was to assess the induction of known aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)-responsive genes in primary human B cells as a measure of early biological responses to TCDD. The second was to evaluate the direct effect of TCDD on CD40 ligand-induced immunoglobulin M (IgM) secretion by human primary B cells. The effects of TCDD on induction of AHR-responsive genes and suppression of the IgM response were also compared with B cells from a TCDD-responsive mouse strain, C57BL/6. AHR-responsive genes in human B cells exhibited slower kinetics and reduced magnitude of induction by TCDD when compared with mouse B cells. Evaluation of B-cell function from 12 donors identified two general phenotypes; the majority of donors exhibited similar sensitivity to suppression by TCDD of the IgM response as mouse B cells, which was not attributable to decreased B-cell proliferation. In a minority of donors, no suppression of the IgM response by TCDD was observed. Although donor-to-donor variation in sensitivity to TCDD was observed, human B cells from the majority of donors evaluated showed impairment of effector function by TCDD. Collectively, data presented in this series of studies demonstrate that TCDD impairs the humoral immunity of humans by directly targeting B cells.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Putative link between transcriptional regulation of IgM expression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/dioxin-responsive enhancer signaling pathway.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Nov;295(2):705-16. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. PMID: 11046109
-
The long winding road toward understanding the molecular mechanisms for B-cell suppression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.Toxicol Sci. 2011 Mar;120 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S171-91. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq324. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Toxicol Sci. 2011. PMID: 20952503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent suppression by 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin of IgM secretion in activated B cells.Mol Pharmacol. 1998 Apr;53(4):623-9. Mol Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9547351
-
Comparative analysis of TCDD-induced AhR-mediated gene expression in human, mouse and rat primary B cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Feb 1;316:95-106. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.11.009. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27913140 Free PMC article.
-
Human response to dioxin: aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) molecular structure, function, and dose-response data for enzyme induction indicate an impaired human AhR.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2006 Mar-Apr;9(2):147-71. doi: 10.1080/15287390500196487. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2006. PMID: 16613807 Review.
Cited by
-
Incorporating population-level genetic variability within laboratory models in toxicology: From the individual to the population.Toxicology. 2018 Feb 15;395:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.12.007. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Toxicology. 2018. PMID: 29275117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of Human Interindividual Variability on the Low-Dose Region of Dose-Response Curve Induced by 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin in Primary B Cells.Toxicol Sci. 2016 Oct;153(2):352-60. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw128. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27473338 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Sensitive Human Immunological Target of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation: CD5+ Innate-Like B Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 15;12:635748. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.635748. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33936048 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-induced activation of the human IGH hs1.2 enhancer: Mutational analysis of putative regulatory binding motifs.Mol Immunol. 2020 Apr;120:164-178. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32146146 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation Suppresses EBF1 and PAX5 and Impairs Human B Lymphopoiesis.J Immunol. 2017 Nov 15;199(10):3504-3515. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700289. Epub 2017 Oct 4. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28978690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan LL, Schlezinger JJ, Shansab M, Sherr DH. CYP1A1 in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-induced B lymphocyte growth suppression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006;342:227–235. - PubMed
-
- Allan LL, Sherr DH. Constitutive activation and environmental chemical induction of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/transcription factor in activated human B lymphocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005;67:1740–1750. - PubMed
-
- Dooley RK, Holsapple MP. Elucidation of cellular targets responsible for tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-induced suppression of antibody responses: I. The role of the B lymphocyte. Immunopharmacology. 1988;16:167–180. - PubMed
-
- Dooley RK, Morris DL, Holsapple MP. Elucidation of cellular targets responsible for tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-induced suppression of antibody responses: II. The role of the T-lymphocyte. Immunopharmacology. 1990;19:47–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

