Is tonic sympathetic vasoconstriction increased in the skeletal muscle vasculature of aged canines?
- PMID: 20702803
- PMCID: PMC2980461
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00194.2010
Is tonic sympathetic vasoconstriction increased in the skeletal muscle vasculature of aged canines?
Abstract
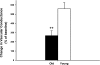
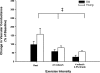
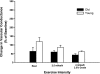
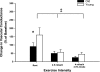
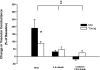
We tested the hypothesis that tonic adrenergic and nonadrenergic receptor-mediated sympathetic vasoconstriction would increase at rest and during exercise with advancing age. Young (n = 6; 22 ± 1 mo; means ± SE) and old (n = 6; 118 ± 9 mo) beagles were studied. Selective antagonists for alpha-1, alpha-2, neuropeptide Y (NPY), and purinergic (P(2x)) receptors were infused at rest and during treadmill running at 2.5 mph and 4 mph with 2.5% grade. Prazosin produced similar increases in vascular conductance in young and old beagles at rest (Young: 158 ± 34%; Old: 98 ± 19%) and during exercise at 2.5 mph (Young: 80 ± 10%; Old: 58 ± 12%) and 4 mph and 2.5% grade (Young: 57 ± 5%; Old: 26 ± 4%). Rauwolscine caused similar (P > 0.05) increases in vascular conductance in old compared with young dogs at rest (Young: 119 ± 25%; Old: 64 ± 22%) and at 2.5 mph (Young: 86 ± 13%; Old: 60 ± 7%) and 4 mph with 2.5% grade (Young: 61 ± 5%; Old: 43 ± 7%). N2-(diphenylacetyl)-N-[4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-d-arginine amide (BIBP) caused a smaller increase (P < 0.05) in vascular conductance in old compared with young dogs at rest (Young: 179 ± 44%; Old: 91 ± 22%), whereas similar increases (P > 0.05) of experimental limb vascular conductance in young and old dogs occurred following BIBP during exercise at 2.5 mph (Young: 56 ± 16%; Old: 50 ± 12%) and 4 mph and 2.5% grade (Young: 45 ± 10%; Old: 25 ± 7%). Pyridoxal-phosphate-6-azophenyl-2'-4'-disulfonic acid infusion produced a larger increase in vascular conductance in old compared with young beagles at rest (Young: 88 ± 14%; Old: 191 ± 58%), whereas similar increases were observed at 2.5 mph (Young: 47 ± 18%; Old: 31 ± 11%) and 4 mph with 2.5% grade (Young: 26 ± 13%; Old: -18 ± 8%). At rest, NPY receptor-mediated restraint of skeletal muscle blood flow was reduced with advancing age, whereas P(2x) receptor-mediated restraint of skeletal muscle blood flow was increased. During exercise, the magnitude of adrenergic and nonadrenergic sympathetic vasoconstriction was not different between young and old dogs. Overall, these data demonstrate that adrenergic receptor-mediated vasoconstriction was not elevated at rest, but nonadrenergic sympathetic vasoconstriction was altered under basal conditions in aged beagles.
Figures
References
-
- Beere PA, Russell SD, Morey MC, Kitzman DW, Higginbotham MB. Aerobic exercise training can reverse age-related peripheral circulatory changes in healthy older men. Circulation 100: 1085–1094, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Bradley E, Law A, Bell D, Johnson CD. Effects of varying impulse number on cotransmitter contributions to sympathetic vasoconstriction in rat tail artery. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284: H2007–H2014, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Buckwalter JB, Clifford PS. The paradox of sympathetic vasoconstriction in exercising skeletal muscle. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 29: 159–163, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Buckwalter JB, Hamann JJ, Clifford PS. Neuropeptide Y1 receptor vasoconstriction in exercising canine skeletal muscles. J Appl Physiol 99: 2115–2120, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Buckwalter JB, Hamann JJ, Clifford PS. Vasoconstriction in active skeletal muscles: a potential role for P2x purinergic receptors? J Appl Physiol 95: 953–959, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

