The treatment of patients with HIV
- PMID: 20703338
- PMCID: PMC2915483
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2010.0507
The treatment of patients with HIV
Abstract
Background: Infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) remains a major medical challenge.
Methods: Selective literature review, including the current German/Austrian, European, and American guidelines on the treatment of HIV infection in adults.
Results: In Germany, 3000 persons become infected with HIV each year; in 2009, 67,000 persons in Germany were living with HIV. When highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) is initiated in time, patients can achieve a nearly normal life expectancy. Nonetheless, in Germany as elsewhere, 30% of patients receive the diagnosis of HIV infection only when they have reached the AIDS stage of the disease or are suffering from advanced immunodeficiency. HAART should be started, at the latest, when the CD4-positive helper cell count drops below 350/microL. Primary drug resistances, accompanying illnesses, and the patient's living circumstances must all be taken into account in the selection of antiretroviral drugs. The goal of treatment is lasting suppression of HIV-RNA to below 50 copies per milliliter of plasma.
Conclusions: HIV testing should be offered to all patients at high risk for HIV infection and all persons newly diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease. As persons with HIV grow older, their treatment is complicated by increasing comorbidity and requires increased vigilance for possible drug interactions.
Figures
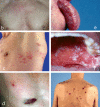
References
-
- Marcus U. Fachgruppe 34 für HIV/AIDS u. a. sexuell oder durch Blut übertragbare Infektionen: Zum Verlauf der HIV-Epidemie in Deutschland bis Ende 2009. Epidemiologisches Bulletin. 2009;(48):491–498.
-
- van Sighem A, Gras L, Reiss P, Brinkman K, de Wolf F. Life expectancy of recently diagnosed asymptomatic HIV-infected patients approaches that of uninfected individuals. AIDS May 12. 2010;24(10):1527–1535. - PubMed
-
- Quinn TC, Wawer MJ, Sewankambo N, et al. Viral load and heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Rakai Project Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(13):921–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

