A comparison of the level of functioning in chronic schizophrenia with coping and burden in caregivers
- PMID: 20703411
- PMCID: PMC2913639
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5545.31615
A comparison of the level of functioning in chronic schizophrenia with coping and burden in caregivers
Abstract
Background: A chronic mental illness such as schizophrenia is a challenging task for caregivers especially in the current era of de-institutionalization. In India, few studies have attempted to directly determine the relationship between coping mechanisms and burden; in the West, studies have found that improved coping in family members can decrease the perceived burden.
Aim: To evaluate the burden and coping of caregivers in relation to the level of functioning in patients with chronic schizophrenia.
Methods: The sample was 100 patients with their primary caregivers attending a Psychiatry OPD. Patients were assessed on the Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) scale while caregivers were administered the Burden Assessment Schedule (BAS) and Mechanisms of Coping (MOC) scale.
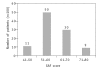
Results: Fatalism and problem-solving were the two most preferred ways of coping. Problem-focused coping, i.e. problem-solving and expressive-action decreased the burden of caregivers, while emotion-focused coping, i.e. fatalism and passivity, increased it. As the level of functioning of the patient decreased, the significance with which the coping mechanisms influenced the burden, increased. The use of problem-solving coping by caregivers showed a significant correlation with higher level of functioning in patients.
Conclusion: Coping mechanisms such as problem-solving can decrease the burden of illness on caregivers and may even improve the level of functioning of patients.
Keywords: Chronic schizophrenia; burden of illness; caregivers; level of functioning; mechanisms of coping.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caregiver burden and coping: a prospective study of relationship between burden and coping in caregivers of patients with schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder.Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2007 Nov;42(11):923-30. doi: 10.1007/s00127-007-0242-8. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2007. PMID: 17700975
-
Relationship of quality of life with coping and burden in primary caregivers of patients with schizophrenia.Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2014 Mar;60(2):107-16. doi: 10.1177/0020764012467598. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 23292614
-
Gender differences in burden of care and coping strategies among caregivers of schizophrenia patients.Ind Psychiatry J. 2023 Jan-Jun;32(1):78-85. doi: 10.4103/ipj.ipj_44_22. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Ind Psychiatry J. 2023. PMID: 37274572 Free PMC article.
-
[Caregiver burden in relatives of persons with schizophrenia: an overview of measure instruments].Encephale. 2003 Mar-Apr;29(2):137-47. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14567165 Review. French.
-
Coping among the caregivers of patients with schizophrenia.Ind Psychiatry J. 2015 Jan-Jun;24(1):5-11. doi: 10.4103/0972-6748.160907. Ind Psychiatry J. 2015. PMID: 26257476 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Caring for the family caregivers of persons with mental illness.Indian J Psychiatry. 2014 Jul;56(3):221-7. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.140616. Indian J Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25316932 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Caregivers in schizophrenia: A cross Cultural Perspective.Indian J Psychol Med. 2010 Jan;32(1):29-33. doi: 10.4103/0253-7176.70526. Indian J Psychol Med. 2010. PMID: 21799556 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy on Resilience among the Wives of Patients with Schizophrenia.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Apr;11(4):VC01-VC03. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/23101.9514. Epub 2017 Apr 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 28571242 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of Indian research in schizophrenia.Indian J Psychiatry. 2010 Jan;52(Suppl 1):S159-72. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.69229. Indian J Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 21836674 Free PMC article.
-
Psychopathology and coping mechanisms in parents of children with intellectual disability.Indian J Psychiatry. 2018 Jul-Sep;60(3):312-317. doi: 10.4103/psychiatry.IndianJPsychiatry_259_17. Indian J Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30405257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kulhara P, Wig NN. The chronicity of schizophrenia in northwest India: Results of a follow-up study. Br J Psychiatry. 1978;132:186–90. - PubMed
-
- Weidmann G, Halweg K, Hank G, et al. Deliverability of psycho-educational social family management. Schizophr Bull. 1994;20:547–56. - PubMed
-
- Provencher HL. Objective burden among primary caregivers of persons with chronic schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Mental Health Nursing. 1996;3(Suppl 3):181–7. - PubMed
-
- Hoenig J, Hamilton MW. The schizophrenic patient in the community and his effect on the household. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 1966;12:165–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials