Characterizing photothrombotic distal middle cerebral artery occlusion and YAG laser-induced reperfusion model in the Izumo strain of spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 20703797
- PMCID: PMC11498362
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-010-9553-5
Characterizing photothrombotic distal middle cerebral artery occlusion and YAG laser-induced reperfusion model in the Izumo strain of spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
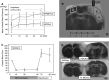
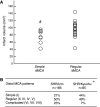
No study has systematically studied the relevance of original Izumo strain of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR/Izm) as a stroke model. Furthermore, both SHR/Izm and stroke-prone SHR/Izm (SHRSP/Izm) are commercially available, and recent progress in genetic studies allowed us to use several congenic strains of rats constructed with SHR/Izm and SHRSP/Izm as the genetic background strains. A total of 166 male SHR/Izm and 17 male SHRSP/Izm were subjected to photothrombotic middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion with or without YAG laser-induced reperfusion. The pattern of distal MCA was recorded. Infarct volumes were determined with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride. At 24 or 48 h after MCA occlusion, infarct volumes in the permanent occlusion and 2-h occlusion groups (88 ± 22 [SD] and 87 ± 25 mm³, respectively) were significantly larger than that in the 1-h occlusion group (45 ± 14 mm³), indicating the presence of sizeable zone of penumbra. Infarct size in SHRSP/Izm determined at 24 h after MCA occlusion was fairly large (124.0 ± 34.8 mm³, n = 10). Infarct volume in SHR/Izm with simple distal MCA was 76 ± 19 mm³, which was significantly smaller than 95 ± 22 mm³ in the other SHR/Izm with more branching MCA. These data suggest that this stroke model in SHR/Izm is useful in the preclinical testing of stroke therapies and elucidating the pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Photothrombotic middle cerebral artery occlusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats: influence of substrain, gender, and distal middle cerebral artery patterns on infarct size.Stroke. 1998 Sep;29(9):1982-6; discussion 1986-7. doi: 10.1161/01.str.29.9.1982. Stroke. 1998. PMID: 9731627
-
Congenic removal of a QTL for blood pressure attenuates infarct size produced by middle cerebral artery occlusion in hypertensive rats.Physiol Genomics. 2007 Jun 19;30(1):69-73. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00149.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 27. Physiol Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17327494
-
Focal Ischemic Injury with Complex Middle Cerebral Artery in Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats with Loss-Of-Function in NADPH Oxidases.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 21;10(9):e0138551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138551. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26389812 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal vulnerability of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats to ischemia and its prevention with antioxidants such as vitamin E.Neuroscience. 2010 Sep 29;170(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.07.013. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20633610 Review.
-
Astrocytic nutritional dysfunction associated with hypoxia-induced neuronal vulnerability in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats.Neurochem Int. 2020 Sep;138:104786. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104786. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Neurochem Int. 2020. PMID: 32579896 Review.
Cited by
-
Excess salt increases infarct size produced by photothrombotic distal middle cerebral artery occlusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats.PLoS One. 2014 May 9;9(5):e97109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097109. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24816928 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of post-ischemic forced use rehabilitation: methods, considerations, and limitations.Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2013 Jan 23;5(1):2. doi: 10.1186/2040-7378-5-2. Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2013. PMID: 23343500 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of stroke.Animal Model Exp Med. 2021 Sep 15;4(3):204-219. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12179. eCollection 2021 Sep. Animal Model Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34557647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Standards and pitfalls of focal ischemia models in spontaneously hypertensive rats: with a systematic review of recent articles.J Transl Med. 2012 Jul 6;10:139. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-139. J Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22770528 Free PMC article.
-
Constructing a Transient Ischemia Attack Model Utilizing Flexible Spatial Targeting Photothrombosis with Real-Time Blood Flow Imaging Feedback.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 10;25(14):7557. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147557. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astrup J, Siesjö BK, Symon L (1981) Thresholds in cerebral ischemia—the ischemic penumbra. Stroke 12:723–725 - PubMed
-
- Baron JC (2001) Perfusion thresholds in human cerebral ischemia: historical perspective and therapeutic implications. Cerebrovasc Dis 11(Suppl 1):2–8 - PubMed
-
- Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski HM (1986) Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke 17:1304–1308 - PubMed
-
- Cai H, Yao H, Ibayashi S, Uchimura H, Fujishima M (1998) Photothrombotic middle cerebral artery occlusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats: influence of substrain, gender and distal middle cerebral artery patterns on infarct size. Stroke 29:1982–1987 - PubMed
-
- Cohen J (1977) The t test for means. In: Cohen J (ed) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc Publishers, Hillsdale, NJ, pp 19–74
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

