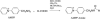Improved sensitivity mass spectrometric detection of eicosanoids by charge reversal derivatization
- PMID: 20704368
- PMCID: PMC2959116
- DOI: 10.1021/ac100720p
Improved sensitivity mass spectrometric detection of eicosanoids by charge reversal derivatization
Abstract
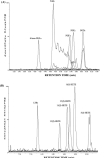
Combined liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS) is a powerful method for the analysis of oxygenated metabolites of polyunsaturated fatty acids including eicosanoids. Here we describe the synthesis of a new derivatization reagent N-(4-aminomethylphenyl)pyridinium (AMPP) that can be coupled to eicosanoids via an amide linkage in quantitative yield. Conversion of the carboxylic acid of eicosanoids to a cationic AMPP amide improves sensitivity of detection by 10- to 20-fold compared to negative mode electrospray ionization detection of underivatized analytes. This charge reversal derivatization allows detection of cations rather than anions in the electrospray ionization mass spectrometer, which enhances sensitivity. Another factor is that AMPP amides undergo considerable collision-induced dissociation in the analyte portion rather than exclusively in the cationic tag portion, which allows isobaric derivatives to be distinguished by tandem mass spectrometry, and this further enhances sensitivity and specificity. This simple derivatization method allows prostaglandins, thromboxane B(2), leukotriene B(4), hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid isomers, and arachidonic acid to be quantified in complex biological samples with limits of quantification in the 200-900 fg range. One can anticipate that the AMPP derivatization method can be extended to other carboxylic acid analytes for enhanced sensitivity detection.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources