School opening dates predict pandemic influenza A(H1N1) outbreaks in the United States
- PMID: 20704486
- PMCID: PMC2939723
- DOI: 10.1086/655810
School opening dates predict pandemic influenza A(H1N1) outbreaks in the United States
Abstract
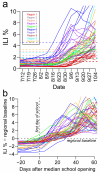
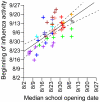
The opening of schools in the late summer of 2009 may have triggered the fall wave of pandemic influenza A(H1N1) in the United States. We found that an elevated percentage of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness occurred an average of 14 days after schools opened in the fall of 2009. The timing of these events was highly correlated (Spearman correlation coefficient, 0.62; P<.001). This result provides evidence that transmission in schools catalyzes community-wide transmission. School opening dates can be useful for future pandemic planning, and influenza mitigation strategies should be targeted at school populations before the influenza season.
Figures
References
-
- Monto AS, Koopman JS, Longini IM., Jr Tecumseh study of illness. XIII. Influenza infection and disease, 1976-1981. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Jun;121(6):811–22. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Update: influenza activity–United States, April-August 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009 Sep 18;58(36):1009–12. - PubMed
-
- Henderson DA, Courtney B, Inglesby TV, Toner E, Nuzzo JB. Public health and medical responses to the 1957-58 influenza pandemic. Biosecur Bioterror. 2009 Sep;7(3):265–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

