Proteomic characterization of an isolated fraction of synthetic proteasome inhibitor (PSI)-induced inclusions in PC12 cells might offer clues to aggresomes as a cellular defensive response against proteasome inhibition by PSI
- PMID: 20704702
- PMCID: PMC2928238
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-95
Proteomic characterization of an isolated fraction of synthetic proteasome inhibitor (PSI)-induced inclusions in PC12 cells might offer clues to aggresomes as a cellular defensive response against proteasome inhibition by PSI
Abstract
Background: Cooperation of constituents of the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) with chaperone proteins in degrading proteins mediate a wide range of cellular processes, such as synaptic function and neurotransmission, gene transcription, protein trafficking, mitochondrial function and metabolism, antioxidant defence mechanisms, and apoptotic signal transduction. It is supposed that constituents of the UPS and chaperone proteins are recruited into aggresomes where aberrant and potentially cytotoxic proteins may be sequestered in an inactive form.
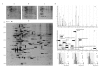
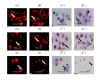
Results: To determinate the proteomic pattern of synthetic proteasome inhibitor (PSI)-induced inclusions in PC12 cells after proteasome inhibition by PSI, we analyzed a fraction of PSI-induced inclusions. A proteomic feature of the isolated fraction was characterized by identification of fifty six proteins including twenty previously reported protein components of Lewy bodies, twenty eight newly identified proteins and eight unknown proteins. These proteins, most of which were recognized as a profile of proteins within cellular processes mediated by the UPS, a profile of constituents of the UPS and a profile of chaperone proteins, are classed into at least nine accepted categories. In addition, prolyl-4-hydroxylase beta polypeptide, an endoplasmic reticulum member of the protein disulfide isomerase family, was validated in the developmental process of PSI-induced inclusions in the cells.
Conclusions: It is speculated that proteomic characterization of an isolated fraction of PSI-induced inclusions in PC12 cells might offer clues to appearance of aggresomes serving as a cellular defensive response against proteasome inhibition.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chaperone proteins identified from synthetic proteasome inhibitor-induced inclusions in PC12 cells by proteomic analysis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2008 May;40(5):406-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7270.2008.00416.x. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2008. PMID: 18465026
-
Proteomic Study of a Parkinson's Disease Model of Undifferentiated SH-SY5Y Cells Induced by a Proteasome Inhibitor.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jan 1;16(1):84-92. doi: 10.7150/ijms.28595. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30662332 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic changes of PC12 cells treated with proteasomal inhibitor PSI.Brain Res. 2007 Jun 11;1153:196-203. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.03.073. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17490626
-
Nucleolar aggresomes as counterparts of cytoplasmic aggresomes in proteotoxic stress. Proteasome inhibitors induce nuclear ribonucleoprotein inclusions that accumulate several key factors of neurodegenerative diseases and cancer.Bioessays. 2011 May;33(5):386-95. doi: 10.1002/bies.201100008. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Bioessays. 2011. PMID: 21425306 Review.
-
Exploring proteasome complexes by proteomic approaches.Proteomics. 2007 Apr;7(7):1047-58. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200600574. Proteomics. 2007. PMID: 17390294 Review.
Cited by
-
Composition of the Intranuclear Inclusions of Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019 Sep 3;7(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0796-1. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31481131 Free PMC article.
-
mPOS is a novel mitochondrial trigger of cell death - implications for neurodegeneration.FEBS Lett. 2018 Mar;592(5):759-775. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12894. Epub 2017 Nov 14. FEBS Lett. 2018. PMID: 29090463 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

