The ubiquitin modifying enzyme A20 restricts B cell survival and prevents autoimmunity
- PMID: 20705491
- PMCID: PMC2931361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.07.017
The ubiquitin modifying enzyme A20 restricts B cell survival and prevents autoimmunity
Abstract
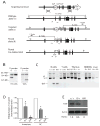
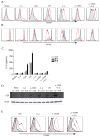
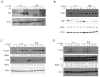
A20 is a ubiquitin modifying enzyme that restricts NF-kappaB signals and protects cells against tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced programmed cell death. Given recent data linking A20 (TNFAIP3) with human B cell lymphomas and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), we have generated mice bearing a floxed allele of Tnfaip3 to interrogate A20's roles in regulating B cell functions. A20-deficient B cells are hyperresponsive to multiple stimuli and display exaggerated NF-kappaB responses to CD40-induced signals. Mice expressing absent or hypomorphic amounts of A20 in B cells possess elevated numbers of germinal center B cells, autoantibodies, and glomerular immunoglobulin deposits. A20-deficient B cells are resistant to Fas-mediated cell death, probably due to increased expression of NF-kappaB-dependent antiapoptotic proteins such as Bcl-x. These findings show that A20 can restrict B cell survival, whereas A20 protects other cells from TNF-induced cell death. Our studies demonstrate how reduced A20 expression predisposes to autoimmunity.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Arvelo MB, Arvelo MB, Cooper JT, Longo C, Daniel S, Grey ST, Mahiou J, Czismadia E, Abu-Jawdeh G, Ferran C. A20 protects mice from D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide acute toxic lethal hepatitis. Hepatology. 2002;35:535–543. - PubMed
-
- Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG, Ahmad RC, Wheeler MT, Tsui C, Hurley P, Chien M, Chai S, Hitotsumatsu O, McNally E, Pickart C, Ma A. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:1052–1060. - PubMed
-
- Coornaert B, Baens M, Heyninck K, Bekaert T, Haegman M, Staal J, Sun L, Chen ZJ, Marynen P, Beyaert R. T cell antigen receptor stimulation induces MALT1 paracaspase-mediated cleavage of the NF-kappaB inhibitor A20. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:263–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

