Elucidation of a novel extracellular calcium-binding site on metabotropic glutamate receptor 1{alpha} (mGluR1{alpha}) that controls receptor activation
- PMID: 20705606
- PMCID: PMC2963343
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.147033
Elucidation of a novel extracellular calcium-binding site on metabotropic glutamate receptor 1{alpha} (mGluR1{alpha}) that controls receptor activation
Abstract
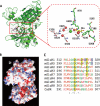
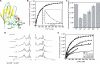
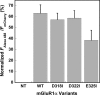
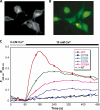
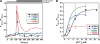
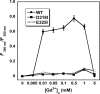
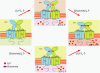
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 1α (mGluR1α) exerts important effects on numerous neurological processes. Although mGluR1α is known to respond to extracellular Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)](o)) and the crystal structures of the extracellular domains (ECDs) of several mGluRs have been determined, the calcium-binding site(s) and structural determinants of Ca(2+)-modulated signaling in the Glu receptor family remain elusive. Here, we identify a novel Ca(2+)-binding site in the mGluR1α ECD using a recently developed computational algorithm. This predicted site (comprising Asp-318, Glu-325, and Asp-322 and the carboxylate side chain of the receptor agonist, Glu) is situated in the hinge region in the ECD of mGluR1α adjacent to the reported Glu-binding site, with Asp-318 involved in both Glu and calcium binding. Mutagenesis studies indicated that binding of Glu and Ca(2+) to their distinct but partially overlapping binding sites synergistically modulated mGluR1α activation of intracellular Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)](i)) signaling. Mutating the Glu-binding site completely abolished Glu signaling while leaving its Ca(2+)-sensing capability largely intact. Mutating the predicted Ca(2+)-binding residues abolished or significantly reduced the sensitivity of mGluR1α not only to [Ca(2+)](o) and [Gd(3+)](o) but also, in some cases, to Glu. The dual activation of mGluR1α by [Ca(2+)](o) and Glu has important implications for the activation of other mGluR subtypes and related receptors. It also opens up new avenues for developing allosteric modulators of mGluR function that target specific human diseases.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Extracellular calcium modulates actions of orthosteric and allosteric ligands on metabotropic glutamate receptor 1α.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 17;289(3):1649-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.507665. Epub 2013 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24280223 Free PMC article.
-
Functional identification of Gd3+ binding site of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1alpha.FEBS Lett. 2003 Jun 19;545(2-3):233-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00569-6. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12804782
-
Dual signaling is differentially activated by different active states of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1alpha.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jan 24;103(4):1124-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505925103. Epub 2006 Jan 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16410359 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the metabotropic glutamate receptor.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003 Jun;13(3):271-8. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(03)00067-9. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 12850210 Review.
-
Calcium dependence of native metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling in central neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2004 Jun;29(3):261-70. doi: 10.1385/MN:29:3:261. Mol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15181238 Review.
Cited by
-
Current perspectives on the neurobiology of drug addiction: a focus on genetics and factors regulating gene expression.ISRN Neurol. 2012;2012:972607. doi: 10.5402/2012/972607. Epub 2012 Oct 14. ISRN Neurol. 2012. PMID: 23097719 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of the Extracellular Ligands Mediated Signaling by the Calcium Sensing Receptor.Front Physiol. 2016 Sep 30;7:441. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00441. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27746744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular calcium modulates actions of orthosteric and allosteric ligands on metabotropic glutamate receptor 1α.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 17;289(3):1649-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.507665. Epub 2013 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24280223 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric modulation of the fish taste receptor type 1 (T1R) family by the extracellular chloride ion.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 28;13(1):16348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43700-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37770555 Free PMC article.
-
Direct determination of multiple ligand interactions with the extracellular domain of the calcium-sensing receptor.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 28;289(48):33529-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.604652. Epub 2014 Oct 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25305020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kano M., Kato M. (1987) Nature 325, 276–279 - PubMed
-
- Kaupmann K., Huggel K., Heid J., Flor P. J., Bischoff S., Mickel S. J., McMaster G., Angst C., Bittiger H., Froestl W., Bettler B. (1997) Nature 386, 239–246 - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi S. (1994) Neuron 13, 1031–1037 - PubMed
-
- Masu M., Tanabe Y., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. (1991) Nature 349, 760–765 - PubMed
-
- Conn P. J., Pin J. P. (1997) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37, 205–237 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

