Streptococcal inhibitor of complement-mediated lysis (SIC): an anti-inflammatory virulence determinant
- PMID: 20705662
- PMCID: PMC7336538
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.039578-0
Streptococcal inhibitor of complement-mediated lysis (SIC): an anti-inflammatory virulence determinant
Abstract
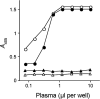
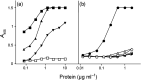
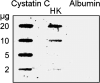
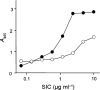
Since the late 1980s, a worldwide increase of severe Streptococcus pyogenes infections has been associated with strains of the M1 serotype, strains which all secrete the streptococcal inhibitor of complement-mediated lysis (SIC). Previous work has shown that SIC blocks complement-mediated haemolysis, inhibits the activity of antibacterial peptides and has affinity for the human plasma proteins clusterin and histidine-rich glycoprotein; the latter is a member of the cystatin protein family. The present work demonstrates that SIC binds to cystatin C, high-molecular-mass kininogen (HK) and low-molecular-mass kininogen, which are additional members of this protein family. The binding sites in HK are located in the cystatin-like domain D3 and the endothelial cell-binding domain D5. Immobilization of HK to cellular structures plays a central role in activation of the human contact system. SIC was found to inhibit the binding of HK to endothelial cells, and to reduce contact activation as measured by prolonged blood clotting time and impaired release of bradykinin. These results suggest that SIC modifies host defence systems, which may contribute to the virulence of S. pyogenes strains of the M1 serotype.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Streptococcal inhibitor of complement (SIC) modulates fibrinolysis and enhances bacterial survival within fibrin clots.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 31;293(35):13578-13591. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.001988. Epub 2018 Jul 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30002122 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial activity of the contact and complement systems is blocked by SIC, a protein secreted by Streptococcus pyogenes.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 14;286(2):1331-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.178350. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21068386 Free PMC article.
-
Protein SIC, a novel extracellular protein of Streptococcus pyogenes interfering with complement function.J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):1081-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.1081. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8557634
-
Catch Me if You Can: Streptococcus pyogenes Complement Evasion Strategies.J Innate Immun. 2019;11(1):3-12. doi: 10.1159/000492944. Epub 2018 Sep 28. J Innate Immun. 2019. PMID: 30269134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteolysis and its regulation at the surface of Streptococcus pyogenes.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Feb;43(3):537-44. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02766.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11929513 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitor of streptokinase gene expression improves survival after group A streptococcus infection in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 28;109(9):3469-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201031109. Epub 2012 Feb 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22331877 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms that potentially contribute to the development of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.Pathog Dis. 2024 Feb 7;82:ftae024. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftae024. Pathog Dis. 2024. PMID: 39341789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunohaemostasis: a new view on haemostasis during sepsis.Ann Intensive Care. 2017 Dec 2;7(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0339-5. Ann Intensive Care. 2017. PMID: 29197958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptococcal inhibitor of complement (SIC) modulates fibrinolysis and enhances bacterial survival within fibrin clots.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 31;293(35):13578-13591. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.001988. Epub 2018 Jul 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30002122 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial activity of the contact and complement systems is blocked by SIC, a protein secreted by Streptococcus pyogenes.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 14;286(2):1331-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.178350. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21068386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahamson M. Cystatins. Methods Enzymol. 1994;244:685–700. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamson M., Barrett A. J., Salvesen G., Grubb A. Isolation of six cysteine proteinase inhibitors from human urine. Their physicochemical and enzyme kinetic properties and concentrations in biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:11282–11289. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamson M., Dalboge H., Olafsson I., Carlsen S., Grubb A. Efficient production of native, biologically active human cystatin C by Escherichia coli . FEBS Lett. 1988;236:14–18. - PubMed
-
- Åkesson P., Cooney J., Kishimoto F., Björck L. Protein H – a novel IgG binding bacterial protein. Mol Immunol. 1990;27:523–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

