Streptococcal inhibitor of complement-mediated lysis (SIC): an anti-inflammatory virulence determinant
- PMID: 20705662
- PMCID: PMC7336538
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.039578-0
Streptococcal inhibitor of complement-mediated lysis (SIC): an anti-inflammatory virulence determinant
Abstract
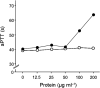
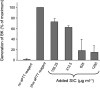
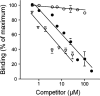
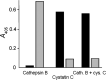
Since the late 1980s, a worldwide increase of severe Streptococcus pyogenes infections has been associated with strains of the M1 serotype, strains which all secrete the streptococcal inhibitor of complement-mediated lysis (SIC). Previous work has shown that SIC blocks complement-mediated haemolysis, inhibits the activity of antibacterial peptides and has affinity for the human plasma proteins clusterin and histidine-rich glycoprotein; the latter is a member of the cystatin protein family. The present work demonstrates that SIC binds to cystatin C, high-molecular-mass kininogen (HK) and low-molecular-mass kininogen, which are additional members of this protein family. The binding sites in HK are located in the cystatin-like domain D3 and the endothelial cell-binding domain D5. Immobilization of HK to cellular structures plays a central role in activation of the human contact system. SIC was found to inhibit the binding of HK to endothelial cells, and to reduce contact activation as measured by prolonged blood clotting time and impaired release of bradykinin. These results suggest that SIC modifies host defence systems, which may contribute to the virulence of S. pyogenes strains of the M1 serotype.
Figures
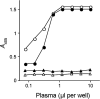
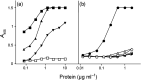
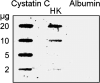
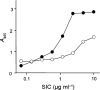
References
-
- Abrahamson M. Cystatins. Methods Enzymol. 1994;244:685–700. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamson M., Barrett A. J., Salvesen G., Grubb A. Isolation of six cysteine proteinase inhibitors from human urine. Their physicochemical and enzyme kinetic properties and concentrations in biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:11282–11289. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamson M., Dalboge H., Olafsson I., Carlsen S., Grubb A. Efficient production of native, biologically active human cystatin C by Escherichia coli . FEBS Lett. 1988;236:14–18. - PubMed
-
- Åkesson P., Cooney J., Kishimoto F., Björck L. Protein H – a novel IgG binding bacterial protein. Mol Immunol. 1990;27:523–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

