Exome sequencing: the sweet spot before whole genomes
- PMID: 20705737
- PMCID: PMC2953745
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq333
Exome sequencing: the sweet spot before whole genomes
Abstract
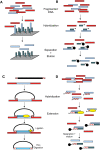
The development of massively parallel sequencing technologies, coupled with new massively parallel DNA enrichment technologies (genomic capture), has allowed the sequencing of targeted regions of the human genome in rapidly increasing numbers of samples. Genomic capture can target specific areas in the genome, including genes of interest and linkage regions, but this limits the study to what is already known. Exome capture allows an unbiased investigation of the complete protein-coding regions in the genome. Researchers can use exome capture to focus on a critical part of the human genome, allowing larger numbers of samples than are currently practical with whole-genome sequencing. In this review, we briefly describe some of the methodologies currently used for genomic and exome capture and highlight recent applications of this technology.
Figures
References
-
- Tarpey P.S., Smith R., Pleasance E., Whibley A., Edkins S., Hardy C., O'Meara S., Latimer C., Dicks E., Menzies A., et al. A systematic, large-scale resequencing screen of X-chromosome coding exons in mental retardation. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:535–543. doi:10.1038/ng.367. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jones S., Zhang X., Parsons D.W., Lin J.C., Leary R.J., Angenendt P., Mankoo P., Carter H., Kamiyama H., Jimeno A., et al. Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses. Science. 2008;321:1801–1806. doi:10.1126/science.1164368. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garber K. Fixing the front end. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008;26:1101–1104. doi:10.1038/nbt1008-1101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Summerer D. Enabling technologies of genomic-scale sequence enrichment for targeted high-throughput sequencing. Genomics. 2009;94:363–368. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2009.08.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Turner E.H., Ng S.B., Nickerson D.A., Shendure J. Methods for genomic partitioning. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2009;10:263–284. doi:10.1146/annurev-genom-082908-150112. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

