Histone H3 Thr-3 phosphorylation by Haspin positions Aurora B at centromeres in mitosis
- PMID: 20705812
- PMCID: PMC2967368
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1189435
Histone H3 Thr-3 phosphorylation by Haspin positions Aurora B at centromeres in mitosis
Abstract
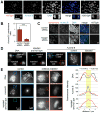
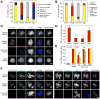
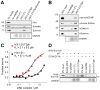
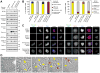
Aurora B is a component of the chromosomal passenger complex (CPC) required for correct spindle-kinetochore attachments during chromosome segregation and for cytokinesis. The chromatin factors that recruit the CPC to centromeres are unknown, however. Here we show that phosphorylation of histone H3 threonine 3 (H3T3ph) by Haspin is necessary for CPC accumulation at centromeres and that the CPC subunit Survivin binds directly to H3T3ph. A nonbinding Survivin-D70A/D71A mutant does not support centromeric CPC concentration, and both Haspin depletion and Survivin-D70A/D71A mutation diminish centromere localization of the kinesin MCAK and the mitotic checkpoint response to taxol. Survivin-D70A/D71A mutation and microinjection of H3T3ph-specific antibody both compromise centromeric Aurora B functions but do not prevent cytokinesis. Therefore, H3T3ph generated by Haspin positions the CPC at centromeres to regulate selected targets of Aurora B during mitosis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Molecular biology. Surfing chromosomes (and Survivin).Science. 2010 Oct 8;330(6001):183-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1197261. Science. 2010. PMID: 20929762 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

