An allosteric self-splicing ribozyme triggered by a bacterial second messenger
- PMID: 20705859
- PMCID: PMC4538695
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1190713
An allosteric self-splicing ribozyme triggered by a bacterial second messenger
Abstract
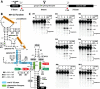
Group I self-splicing ribozymes commonly function as components of selfish mobile genetic elements. We identified an allosteric group I ribozyme, wherein self-splicing is regulated by a distinct riboswitch class that senses the bacterial second messenger c-di-GMP. The tandem RNA sensory system resides in the 5' untranslated region of the messenger RNA for a putative virulence gene in the pathogenic bacterium Clostridium difficile. c-di-GMP binding by the riboswitch induces folding changes at atypical splice site junctions to modulate alternative RNA processing. Our findings indicate that some self-splicing ribozymes are not selfish elements but are harnessed by cells as metabolite sensors and genetic regulators.
Figures


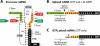
Similar articles
-
Mechanism for gene control by a natural allosteric group I ribozyme.RNA. 2011 Nov;17(11):1967-72. doi: 10.1261/rna.2757311. Epub 2011 Sep 29. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21960486 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro selection of allosteric ribozymes that sense the bacterial second messenger c-di-GMP.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1111:209-20. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-755-6_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24549622 Free PMC article.
-
Riboswitches in eubacteria sense the second messenger cyclic di-GMP.Science. 2008 Jul 18;321(5887):411-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1159519. Science. 2008. PMID: 18635805 Free PMC article.
-
[Structure and function of c-di-GMP riboswitches].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2017 Sep 25;33(9):1357-1368. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.170085. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 28956387 Review. Chinese.
-
Base ionization and ligand binding: how small ribozymes and riboswitches gain a foothold in a protein world.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011 Jun;21(3):327-34. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2011.03.016. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 21530235 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclic-di-GMP signaling in the Gram-positive pathogen Clostridium difficile.Curr Genet. 2015 Nov;61(4):497-502. doi: 10.1007/s00294-015-0484-z. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Curr Genet. 2015. PMID: 25800812 Review.
-
Synthetic Biology of Small RNAs and Riboswitches.Microbiol Spectr. 2018 May;6(3):10.1128/microbiolspec.rwr-0007-2017. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.RWR-0007-2017. Microbiol Spectr. 2018. PMID: 29932045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular Imaging with Genetically Encoded RNA-based Molecular Sensors.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Feb 8;9(2):233. doi: 10.3390/nano9020233. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30744040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of the c-di-GMP riboswitch with its second messenger ligand.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Apr;39(2):647-51. doi: 10.1042/BST0390647. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21428955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering modular 'ON' RNA switches using biological components.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Dec;41(22):10449-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt787. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23999097 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

