The effect of class II transactivator mutations on bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis
- PMID: 20705943
- PMCID: PMC3135849
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0416OC
The effect of class II transactivator mutations on bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis
Abstract
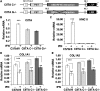
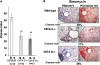
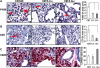
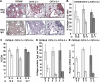
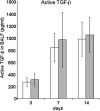
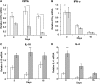
IFN-γ expression increases during the inflammatory response after bleomycin injury in mice. IFN-γ deficiency attenuates lung inflammation and fibrosis. Because IFN-γ stimulates class II transactivator (CIITA) expression, which activates major histocompatibility class (MHC) II and represses collagen expression, it was hypothesized that CIITA mediates IFN-γ action after bleomycin injury. To test this hypothesis, two CIITA mouse lines, one carrying a mutation of the leucine-rich region of CIITA (CIITA C-/-) and one with a deletion extending into the GTP-binding domain (CIITA G-/-), were used. IFN-γ treatment of lung cells isolated from both strains of mice induced mutant CIITA expression, which did not activate MHC II transcription. Collagen expression was similar in both mutant mouse strains and comparable to C57BL/6 (wild-type) mice. When mice were exposed to intratracheal bleomycin, both strains of CIITA mutant mice retained body weight and altered inflammation at 14 days after bleomycin injury compared with bleomycin-treated wild-type mice. However, there was no difference in fibrosis as judged by histology, mRNA, and protein expression of lungs. Bronchoalveolar lavage cells from CIITA C-/- and C57BL/6 lungs were examined at 3, 7, and 14 days after bleomycin injury. CD4 mRNA expression in bronchoalveolar lavage cells was down-regulated, whereas IL-4 and IL-10 expression was up-regulated, in CIITA C-/- mice, indicating a diminished, skewed Th2 response. The expression of IFN-γ was the same in all mice tested. Combined, our data suggest that CIITA mutations altered the immune response without affecting fibrosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Collagen and major histocompatibility class II expression in mesenchymal cells from CIITA hypomorphic mice.Mol Immunol. 2007 Mar;44(7):1709-21. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.07.294. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 16982097
-
Reduced IL-4-, lipopolysaccharide-, and IFN-gamma-induced MHC class II expression in mice lacking class II transactivator due to targeted deletion of the GTP-binding domain.J Immunol. 1999 Sep 1;163(5):2425-31. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10452977
-
Major histocompatibility class II transactivator (CIITA) mediates repression of collagen (COL1A2) transcription by interferon gamma (IFN-gamma).J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 1;279(40):41319-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404174200. Epub 2004 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15247294
-
Interferon-gamma induces major histocompatibility class II transactivator (CIITA), which mediates collagen repression and major histocompatibility class II activation by human aortic smooth muscle cells.Circ Res. 2006 Mar 3;98(4):472-9. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000204725.46332.97. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Circ Res. 2006. PMID: 16439692 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon (IFN) beta acts downstream of IFN-gamma-induced class II transactivator messenger RNA accumulation to block major histocompatibility complex class II gene expression and requires the 48-kD DNA-binding protein, ISGF3-gamma.J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1517-25. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1517. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7595221 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Resident Fibroblast MKL1 Is Sufficient to Drive Pro-fibrogenic Response in Mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 1;9:812748. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.812748. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35178401 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of hydroxycamptothecin and pingyangmycin on human squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue.Oncol Lett. 2013 Mar;5(3):947-952. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1109. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23426884 Free PMC article.
-
Protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) represses MHC II transcription in macrophages by methylating CIITA.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 17;7:40531. doi: 10.1038/srep40531. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28094290 Free PMC article.
-
Megakaryocytic leukemia 1 (MKL1) regulates hypoxia induced pulmonary hypertension in rats.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 19;9(3):e83895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083895. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24647044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moore BB, Hogaboam CM. Murine models of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2008;294:L152–L160. - PubMed
-
- Lotze MT, Zeh HJ, Rubartelli A, Sparvero LJ, Amoscato AA, Washburn NR, Devera ME, Liang X, Tor M, Billiar T. The grateful dead: damage-associated molecular pattern molecules and reduction/oxidation regulate immunity. Immunol Rev 2007;220:60–81. - PubMed
-
- Harton JA, Linhoff MW, Zhang J, Ting JP. Cutting edge: CATERPILLER: a large family of mammalian genes containing CARD, pyrin, nucleotide-binding, and leucine-rich repeat domains. J Immunol 2002;169:4088–4093. - PubMed
-
- Reith W, Mach B. The bare lymphocyte syndrome and the regulation of MHC expression. Annu Rev Immunol 2001;19:331–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

