Rituximab therapy in idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a 2-year study
- PMID: 20705965
- PMCID: PMC2994079
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05080610
Rituximab therapy in idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a 2-year study
Abstract
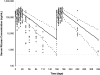
Background and objectives: It was postulated that in patients with membranous nephropathy (MN), four weekly doses of Rituximab (RTX) would result in more effective B cell depletion, a higher remission rate, and maintaining the same safety profile compared with patients treated with RTX dosed at 1 g every 2 weeks. This hypothesis was supported by previous pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis showing that RTX levels in the two-dose regimen were 50% lower compared with nonproteinuric patients, which could potentially result in undertreatment.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Twenty patients with MN and proteinuria >5 g/24 h received RTX (375 mg/m(2) × 4), with re-treatment at 6 months regardless of proteinuria response. PK analysis was conducted simultaneously with immunological analyses of T and B cells to ascertain the effect of RTX on lymphocyte subpopulations.
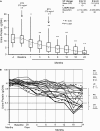
Results: Baseline proteinuria of 11.9 g/24 h decreased to 4.2 and 2.0 g/24 h at 12 and 24 months, respectively, whereas creatinine clearance increased from 72.4 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) at baseline to 88.4 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) at 24 months. Of 18 patients who completed 24-month follow-up, 4 are in complete remission, 12 are in partial remission, 1 has a limited response, and 1 patient relapsed. Serum RTX levels were similar to those obtained with two doses of RTX.
Conclusions: Four doses of RTX resulted in more effective B cell depletion, but proteinuria reduction was similar to RTX at 1 g every 2 weeks. Baseline quantification of lymphocyte subpopulations did not predict response to RTX therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Fervenza FC, Cosio FG, Erickson SB, Specks U, Herzenberg AM, Dillon JJ, Leung N, Cohen IM, Wochos DN, Bergstralh E, Hladunewich M, Cattran DC: Rituximab treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 73: 117–125, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Looney RJ, Anolik JH, Campbell D, Felgar RE, Young F, Arend LJ, Sloand JA, Rosenblatt J, Sanz I: B cell depletion as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus: A phase I/II dose-escalation trial of rituximab. Arthritis Rheum 50: 2580–2589, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Leandro MJ, Cambridge G, Ehrenstein MR, Edwards JC: Reconstitution of peripheral blood B cells after depletion with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54: 613–620, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Popa ER, Stegeman CA, Bos NA, Kallenberg CG, Tervaert JW: Differential B- and T-cell activation in Wegener's granulomatosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 103: 885–894, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

