The use of aluminum nanostructures as platforms for metal enhanced fluorescence of the intrinsic emission of biomolecules in the ultra-violet
- PMID: 20706552
- PMCID: PMC2919809
- DOI: 10.1117/12.841449
The use of aluminum nanostructures as platforms for metal enhanced fluorescence of the intrinsic emission of biomolecules in the ultra-violet
Abstract
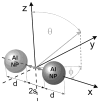
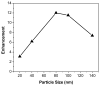
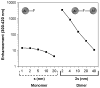
We consider the possibility of using aluminum nanostructures for enhancing the intrinsic emission of biomolecules. We used the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method to calculate the effects of aluminum nanoparticles on nearby fluorophores that emit in the ultra-violet (UV). We find that the radiated power of UV fluorophores is significantly increased when they are in close proximity to aluminum nanostructures. We show that there will be increased localized excitation near aluminum particles at wavelengths used to excite intrinsic biomolecule emission. We also examine the effect of excited-state fluorophores on the near-field around the nanoparticles. Finally we present experimental evidence showing that a thin film of amino acids and nucleotides display enhanced emission when in close proximity to aluminum nanostructured surfaces. Our results suggest that biomolecules can be detected and identified using aluminum nanostructures that enhance their intrinsic emission. We hope this study will ignite interest in the broader scientific community to take advantage of the plasmonic properties of aluminum and the potential benefits of its interaction with biomolecules to generate momentum towards implementing fluorescence-based bioassays using their intrinsic emission.
Figures


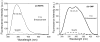
Similar articles
-
On the Feasibility of Using the Intrinsic Fluorescence of Nucleotides for DNA Sequencing.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2010 Apr 29;114(16):7448-7461. doi: 10.1021/jp911229c. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2010. PMID: 20436924 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-enhanced Intrinsic Fluorescence of Proteins on Silver Nanostructured Surfaces towards Label-Free Detection.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2008;112(46):17957-17963. doi: 10.1021/jp807025n. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2008. PMID: 19180253 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of Using Bimetallic Plasmonic Nanostructures to Enhance the Intrinsic Emission of Biomolecules.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2011 Sep 1;115(34):16879-16891. doi: 10.1021/jp205108s. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2011. PMID: 21984954 Free PMC article.
-
Metal enhanced fluorescence biosensing: from ultra-violet towards second near-infrared window.Nanoscale. 2018 Dec 7;10(45):20914-20929. doi: 10.1039/c8nr06156d. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Nanoscale. 2018. PMID: 30324956 Review.
-
Plasmon-controlled fluorescence: a new paradigm in fluorescence spectroscopy.Analyst. 2008 Oct;133(10):1308-46. doi: 10.1039/b802918k. Epub 2008 Jul 16. Analyst. 2008. PMID: 18810279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lakowicz JR. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy. 3. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; New York: 2006.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
