Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha, Beta, and gamma mRNA and protein expression in human fetal tissues
- PMID: 20706641
- PMCID: PMC2913814
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/690907
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha, Beta, and gamma mRNA and protein expression in human fetal tissues
Erratum in
- PPAR Res. 2010;2010:627284
Abstract
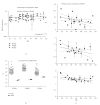
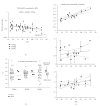
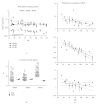
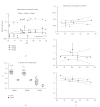
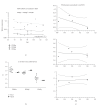
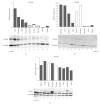
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) regulate lipid and glucose homeostasis, are targets of pharmaceuticals, and are also activated by environmental contaminants. Almost nothing is known about expression of PPARs during human fetal development. This study examines expression of PPARalpha, beta, and gamma mRNA and protein in human fetal tissues. With increasing fetal age, mRNA expression of PPARalpha and beta increased in liver, but PPARbeta decreased in heart and intestine, and PPARgamma decreased in adrenal. Adult and fetal mean expression of PPARalpha, beta, and gamma mRNA did not differ in intestine, but expression was lower in fetal stomach and heart. PPARalpha and beta mRNA in kidney and spleen, and PPARgamma mRNA in lung and adrenal were lower in fetal versus adult. PPARgamma in liver and PPARbeta mRNA in thymus were higher in fetal versus adult. PPARalpha protein increased with fetal age in intestine and decreased in lung, kidney, and adrenal. PPARbeta protein in adrenal and PPARgamma in kidney decreased with fetal age. This study provides new information on expression of PPAR subtypes during human development and will be important in evaluating the potential for the developing human to respond to PPAR environmental or pharmaceutical agonists.
Figures




References
-
- Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocrine Reviews. 1999;20(5):649–688. - PubMed
-
- Keller H, Devchand PR, Perroud M, Wahli W. PPARα structure-function relationships derived from species-specific differences in responsiveness to hypolipidemic agents. Biological Chemistry. 1997;378(7):651–655. - PubMed
-
- Michalik L, Desvergne B, Dreyer C, Gavillet M, Laurini RN, Wahli W. PPAR expression and function during vertebrate development. International Journal of Developmental Biology. 2002;46(1):105–114. - PubMed
-
- Escher P, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: insight into multiple cellular functions. Mutation Research. 2000;448(2):121–138. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

