Paraneoplastic pemphigus presenting as mild cutaneous features of pemphigus foliaceus and lichenoid stomatitis with antidesmoglein 1 antibodies
- PMID: 20706645
- PMCID: PMC2913839
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/931340
Paraneoplastic pemphigus presenting as mild cutaneous features of pemphigus foliaceus and lichenoid stomatitis with antidesmoglein 1 antibodies
Abstract
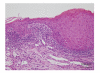
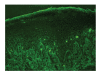
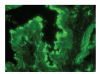
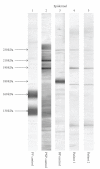
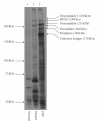
Herein, we report a case of paraneoplastic pemphigus with mild skin features of pemphigus foliaceus and lichenoid stomatitis associated with B-cell lymphoma. A 49-year-old man presented with scattered blisters and erosions on the trunk along with mucosal blisters and erosions. Skin biopsy showed subcorneal acantholytic bulla and oral mucosal biopsy demonstrated lichenoid dermatitis. Direct immunofluorescence showed cell surface deposits of IgG and C3. Indirect immunofluorescence identified circulating IgG autoantibodies to the cell surfaces of normal human skin and also on the transitional epithelium of rat bladder. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant baculoproteins showed positive antidesmoglein 1 autoantibodies (index 46) but negative antidesmoglein 3 autoantibodies (index 8). Immunoblot analysis using normal human epidermal extract detected BP230 and the 190 kDa periplakin, while immunoprecipitation using radiolabeled cultured keratinocyte immunoprecipitated BP230 and the 210 kDa envoplakin. We consider that the skin lesion was produced by humoral immunity whereas the oral lesion was produced by cellular immunity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Paraneoplastic pemphigus in children and adolescents.Br J Dermatol. 2002 Oct;147(4):725-32. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04992.x. Br J Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 12366419
-
230-kDa and 190-kDa proteins in addition to desmoglein 1 as immunological targets in a subset of pemphigus foliaceus with a combined cell-surface and basement membrane zone immune staining pattern.Exp Dermatol. 2003 Oct;12(5):646-54. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0625.2003.00103.x. Exp Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 14705806
-
Paraneoplastic pemphigus presenting as erythrodermic lichenoid dermatitis with concomitant features of pemphigus foliaceus.J Dermatol. 2007 Sep;34(9):645-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2007.00347.x. J Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17727368
-
Paraneoplastic pemphigus in association with a retroperitoneal Castleman's disease presenting with a lichen planus pemphigoides-like eruption. A case report and review of literature.Br J Dermatol. 2001 Feb;144(2):372-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04030.x. Br J Dermatol. 2001. PMID: 11251576 Review.
-
IgG/IgA pemphigus with IgG and IgA antidesmoglein 1 antibodies detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.Br J Dermatol. 2002 Nov;147(5):1012-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04984.x. Br J Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 12410717 Review.
Cited by
-
Oral manifestations of systemic disease.Br Dent J. 2017 Nov 10;223(9):683-691. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2017.884. Br Dent J. 2017. PMID: 29123296 Review.
References
-
- Anhalt GJ, Kim SC, Stanley JR, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. An autoimmune mucocutaneous disease associated with neoplasia. New England Journal of Medicine. 1990;323(25):1729–1735. - PubMed
-
- Anhalt GJ. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2004;9(1):29–33. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto T, Amagai M, Watanabe K, et al. Characterization of paraneoplastic pemphigus autoantigens by immunoblot analysis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1995;104(5):829–834. - PubMed
-
- Camisa C, Helm TN. Paraneoplastic pemphigus is a distinct neoplasia-induced autoimmune disease. Archives of Dermatology. 1993;129(7):883–886. - PubMed
-
- Joly P, Richard C, Gilbert D, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of clinical, histologic, and immunologic features in the diagnosis of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2000;43(4):619–626. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

