Effects of assisted reproduction technology on placental imprinted gene expression
- PMID: 20706653
- PMCID: PMC2913850
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/437528
Effects of assisted reproduction technology on placental imprinted gene expression
Abstract
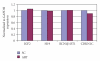
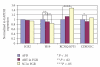
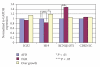
We used placental tissue to compare the imprinted gene expression of IGF2, H19, KCNQ1OT1, and CDKN1C of singletons conceived via assisted reproduction technology (ART) with that of spontaneously conceived (SC) singletons. Of 989 singletons examined (ART n = 65; SC n = 924), neonatal weight was significantly lower (P < .001) in the ART group than in the SC group, but placental weight showed no significant difference. Gene expression analyzed by real-time PCR was similar for both groups with appropriate-for-date (AFD) birth weight. H19 expression was suppressed in fetal growth retardation (FGR) cases in the ART and SC groups compared with AFD cases (P < .02 and P < .05, resp.). In contrast, CDKN1C expression was suppressed in FGR cases in the ART group (P < .01), while KCNQ1OT1 expression was hyperexpressed in FGR cases in the SC group (P < .05). As imprinted gene expression patterns differed between the ART and SC groups, we speculate that ART modifies epigenetic status even though the possibilities always exist.
Figures
References
-
- Maher ER. Imprinting and assisted reproductive technology. Human Molecular Genetics. 2005;14(1):R133–R138. - PubMed
-
- Allen C, Reardon W. Assisted reproduction technology and defects of genomic imprinting. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 2005;112(12):1589–1594. - PubMed
-
- Bonduelle M, Desmyttere S, Buysse A, et al. Prospective follow-up study of 55 children born after subzonal insemination and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Human Reproduction. 1994;9(9):1765–1769. - PubMed
-
- Bonduelle M, Legein J, Derde M-P, et al. Comparative follow-up study of 130 children born after intracytoplasmic sperm injection and 130 children born after in-vitro fertilization. Human Reproduction. 1995;10(12):3327–3331. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

