Regulatory effect of melatonin on cytokine disturbances in the pristane-induced lupus mice
- PMID: 20706659
- PMCID: PMC2913856
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/951210
Regulatory effect of melatonin on cytokine disturbances in the pristane-induced lupus mice
Abstract
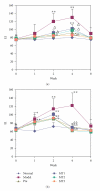
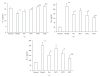
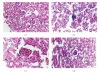
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) develops in relation to many environmental factors. In our opinion, it is more important to investigate the effect of melatonin on the environmental- related SLE. In the present study, 0.5 ml pristane were used to induce SLE in female BALB/c mice. Melatonin (0.01, 0.1, 1.0 mg/kg) was orally administered immediately after pristane-injection for 24 weeks. IgM anti ssDNA and histone antibodies were detected after 0, 1, 2, 4, 8 weeks pristane injection. The levels of IL-2, IL-6 and IL-13 were detected after 24 weeks. Renal lesions were also observed. The results showed that melatonin antagonized the increasing levels of IgM anti ssDNA and histone autoantibodies. Melatonin could also decrease the IL-6 and IL-13 production and increase the IL-2 production. Besides, melatonin could lessen the renal lesions caused by pristane. These results suggested that melatonin has a beneficial effect on pristane-induced lupus through regulating the cytokines disturbances.
Figures
Similar articles
-
X-linked immunodeficient mice spontaneously produce lupus-related anti-RNA helicase A autoantibodies, but are resistant to pristane-induced lupus.Int Immunol. 2003 Sep;15(9):1117-24. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxg110. Int Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12917264
-
The potential protective role of hepatitis B virus infection in pristane-induced lupus in mice.Lupus. 2016 Oct;25(11):1180-9. doi: 10.1177/0961203316631637. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Lupus. 2016. PMID: 27125291
-
Disparate T cell requirements of two subsets of lupus-specific autoantibodies in pristane-treated mice.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Mar;115(3):547-53. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00825.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10193432 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of regulatory T cells by Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Lactobacillus rhamnosus in pristane-induced lupus mice model.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):9778-9786. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27663. Epub 2018 Oct 28. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30370554
-
Pristane-induced lupus: considerations on this experimental model.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Nov;36(11):2403-2414. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3811-6. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28879482 Review.
Cited by
-
UBC4: A Repurposed Drug Regimen for Adjunctive Use During Bladder Cancer Treatment.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 13;13(3):706. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030706. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salvianolic acid A alleviates renal injury in systemic lupus erythematosus induced by pristane in BALB/c mice.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2017 Mar;7(2):159-166. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2017. PMID: 28303221 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation by melatonin of the pathogenesis of inflammatory autoimmune diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 31;14(6):11742-66. doi: 10.3390/ijms140611742. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23727938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin exerts immunoregulatory effects by balancing peripheral effector and regulatory T helper cells in myasthenia gravis.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Nov 2;12(21):21147-21160. doi: 10.18632/aging.103785. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33136553 Free PMC article.
-
Methyl salicylate 2-O-β-d-lactoside alleviates the pathological progression of pristane-induced systemic lupus erythematosus-like disease in mice via suppression of inflammatory response and signal transduction.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Sep 29;10:3183-3196. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S114501. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27729775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsukamoto H, Horiuchi T, Kokuba H, et al. Molecular analysis of a novel hereditary C3 deficiency with systemic lupus erythematosus. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2005;330(1):298–304. - PubMed
-
- Manson JJ, Isenberg DA. The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. The Netherlands Journal of Medicine. 2003;61(11):343–346. - PubMed
-
- El-Magadmi M, Bodill H, Ahmad Y, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus: an independent risk factor for endothelial dysfunction in women. Circulation. 2004;110(4):399–404. - PubMed
-
- Lahita RG. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons; 1986. Sex and age in systemic lupus erythematosus; pp. 523–539.
-
- Jones BM, Liu T, Wong RWS. Reduced in vitro production of inter- feron-gamma, interleukin-4 and interleukin-12 and increased production of interleukin- 6, interleukin-10 and tumor factor-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Weak correlations of cytokine production with disease activity. Autoimmunity. 1999;31(2):117–124. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

