Genetic validation of whole-transcriptome sequencing for mapping expression affected by cis-regulatory variation
- PMID: 20707912
- PMCID: PMC3091669
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-473
Genetic validation of whole-transcriptome sequencing for mapping expression affected by cis-regulatory variation
Abstract
Background: Identifying associations between genotypes and gene expression levels using microarrays has enabled systematic interrogation of regulatory variation underlying complex phenotypes. This approach has vast potential for functional characterization of disease states, but its prohibitive cost, given hundreds to thousands of individual samples from populations have to be genotyped and expression profiled, has limited its widespread application.
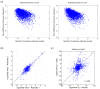
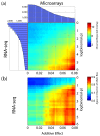
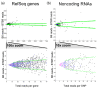
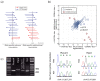
Results: Here we demonstrate that genomic regions with allele-specific expression (ASE) detected by sequencing cDNA are highly enriched for cis-acting expression quantitative trait loci (cis-eQTL) identified by profiling of 500 animals in parallel, with up to 90% agreement on the allele that is preferentially expressed. We also observed widespread noncoding and antisense ASE and identified several allele-specific alternative splicing variants.
Conclusion: Monitoring ASE by sequencing cDNA from as little as one sample is a practical alternative to expression genetics for mapping cis-acting variation that regulates RNA transcription and processing.
Figures
References
-
- Gibson G, Weir B. The quantitative genetics of transcription. Trends Genet. 2005;21(11):616–623. - PubMed
-
- Emilsson V, Thorleifsson G, Zhang B, Leonardson AS, Zink F, Zhu J, Carlson S, Helgason A, Walters GB, Gunnarsdottir S. et al.Genetics of gene expression and its effect on disease. Nature. 2008;452(7186):423–428. - PubMed
-
- Fraser HB, Xie X. Common polymorphic transcript variation in human disease. Genome Res. 2009;19(4):567–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

