The NRF2-mediated oxidative stress response pathway is associated with tumor cell resistance to arsenic trioxide across the NCI-60 panel
- PMID: 20707922
- PMCID: PMC2939609
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-3-37
The NRF2-mediated oxidative stress response pathway is associated with tumor cell resistance to arsenic trioxide across the NCI-60 panel
Abstract
Background: Drinking water contaminated with inorganic arsenic is associated with increased risk for different types of cancer. Paradoxically, arsenic trioxide can also be used to induce remission in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) with a success rate of approximately 80%. A comprehensive study examining the mechanisms and potential signaling pathways contributing to the anti-tumor properties of arsenic trioxide has not been carried out.
Methods: Here we applied a systems biology approach to identify gene biomarkers that underlie tumor cell responses to arsenic-induced cytotoxicity. The baseline gene expression levels of 14,500 well characterized human genes were associated with the GI50 data of the NCI-60 tumor cell line panel from the developmental therapeutics program (DTP) database. Selected biomarkers were tested in vitro for the ability to influence tumor susceptibility to arsenic trioxide.
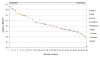
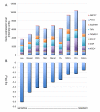
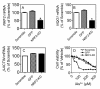
Results: A significant association was found between the baseline expression levels of 209 human genes and the sensitivity of the tumor cell line panel upon exposure to arsenic trioxide. These genes were overlayed onto protein-protein network maps to identify transcriptional networks that modulate tumor cell responses to arsenic trioxide. The analysis revealed a significant enrichment for the oxidative stress response pathway mediated by nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) with high expression in arsenic resistant tumor cell lines. The role of the NRF2 pathway in protecting cells against arsenic-induced cell killing was validated in tumor cells using shRNA-mediated knock-down.
Conclusions: In this study, we show that the expression level of genes in the NRF2 pathway serve as potential gene biomarkers of tumor cell responses to arsenic trioxide. Importantly, we demonstrate that tumor cells that are deficient for NRF2 display increased sensitivity to arsenic trioxide. The results of our study will be useful in understanding the mechanism of arsenic-induced cytotoxicity in cells, as well as the increased applicability of arsenic trioxide as a chemotherapeutic agent in cancer treatment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nrf2 activation ameliorates cytotoxic effects of arsenic trioxide in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells through increased glutathione levels and arsenic efflux from cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 15;305:161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.06.017. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27317373
-
Insight into the selectivity of arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia cells by characterizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae deletion strains that are sensitive or resistant to the metalloid.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(5):1016-29. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.11.002. Epub 2007 Nov 13. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18160327
-
Activation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway Involving KLF9 Plays a Critical Role in Allicin Resisting Against Arsenic Trioxide-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017 Mar;176(1):192-200. doi: 10.1007/s12011-016-0821-1. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017. PMID: 27561292
-
Inhibition factors of arsenic trioxide therapeutic effects in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia.Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(19):3503-6. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014. PMID: 25269921 Review.
-
Arsenic-induced apoptosis in malignant cells in vitro.Leuk Lymphoma. 2000 Mar;37(1-2):53-63. doi: 10.3109/10428190009057628. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000. PMID: 10721769 Review.
Cited by
-
Control of Oxidative Stress in Cancer Chemoresistance: Spotlight on Nrf2 Role.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 25;10(4):510. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040510. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lutein has a protective effect on hepatotoxicity induced by arsenic via Nrf2 signaling.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:315205. doi: 10.1155/2015/315205. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25815309 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of NRF2 signaling overcomes acquired resistance to arsenic trioxide in FLT3-mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Ann Hematol. 2024 Jun;103(6):1919-1929. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05742-8. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38630133
-
Factors determining sensitivity and resistance of tumor cells to arsenic trioxide.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e35584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035584. Epub 2012 May 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22590507 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Activity of Rosmarinus officinalis L.: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Potentials.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 10;12(6):1739. doi: 10.3390/nu12061739. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32532056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guha Mazumder DN. Chronic arsenic toxicity & human health. Indian J Med Res. 2008;128(4):436–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

