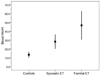
Relationship between blood harmane and harmine concentrations in familial essential tremor, sporadic essential tremor and controls
- PMID: 20708029
- PMCID: PMC2974038
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2010.08.003
Relationship between blood harmane and harmine concentrations in familial essential tremor, sporadic essential tremor and controls
Abstract
Introduction: Harmane, a potent tremor-producing β-carboline alkaloid, may play a role in the etiology of essential tremor (ET). Blood harmane concentrations are elevated in ET cases compared with controls yet the basis for this elevation remains unknown. Decreased metabolic conversion (harmane to harmine) is one possible explanation. Using a sample of >500 individuals, we hypothesized that defective metabolic conversion of harmane to harmine might underlie the observed elevated harmane concentration in ET, and therefore expected to find a higher harmane to harmine ratio in familial ET than in sporadic ET or controls.
Methods: Blood harmane and harmine concentrations were quantified by high performance liquid chromatography.
Results: There were 78 familial ET cases, 187 sporadic ET cases, and 276 controls. Blood harmane and harmine concentrations were correlated with one another (Spearman's r=0.24, p<0.001). The mean (±SD) harmane/harmine ratio=23.4±90.9 (range=0.1-987.5). The harmane/harmine ratio was highest in familial ET (46.7±140.4), intermediate in sporadic ET (28.3±108.1), and lowest in controls (13.5±50.3) (p=0.03). In familial ET cases, there was no association between this ratio and tremor severity (Spearman's r=0.08, p=0.48) or tremor duration (Spearman's r=0.14, p=0.24).
Conclusion: The basis for the elevated blood harmane concentration, particularly in familial ET, is not known, although the current findings (highest harmane/harmine ratio in familial ET cases) lends support to the possibility that it could be the result of a genetically-driven reduction in harmane metabolism.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dogu O, Sevim S, Camdeviren H, et al. Prevalence of essential tremor: door-to-door neurologic exams in Mersin Province, Turkey. Neurology. 2003;61(12):1804–1806. - PubMed
-
- Benito-Leon J, Bermejo-Pareja F, Morales JM, Vega S, Molina JA. Prevalence of essential tremor in three elderly populations of central Spain. Mov Disord. 2003;18(4):389–394. - PubMed
-
- Louis ED, Ferreira JJ. How common is the most common adult movement disorder? Update on the worldwide prevalence of essential tremor. Mov Disord. 2010;25:534–541. - PubMed
-
- Benito-Leon J, Louis ED, Bermejo-Pareja F. Population-based case-control study of cognitive function in essential tremor. Neurology. 2006;66(1):69–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources