Functional integration of new neurons into hippocampal networks and poststroke comorbidities following neonatal stroke in mice
- PMID: 20708575
- PMCID: PMC2923452
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2010.05.006
Functional integration of new neurons into hippocampal networks and poststroke comorbidities following neonatal stroke in mice
Abstract
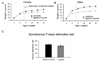
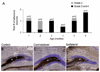
Stroke in the developing brain is an important cause of chronic neurological morbidities including neurobehavioral dysfunction and epilepsy. Here, we describe a mouse model of neonatal stroke resulting from unilateral carotid ligation that results in acute seizures, long-term hyperactivity, spontaneous lateralized circling behavior, impaired cognitive function, and epilepsy. Exploration-dependent induction of the immediate early gene Arc (activity-regulated cytoskeleton associated protein) in hippocampal neurons was examined in the general population of neurons versus neurons that were generated approximately 1 week after the ischemic insult and labeled with bromodeoxyuridine. Although Arc was inducible in a network-specific manner after severe neonatal stroke, it was impaired, not only in the ipsilateral injured but also in the contralateral uninjured hippocampi when examined 6 months after the neonatal stroke. Severity of both the stroke injury and the acquired poststroke epilepsy negatively correlated with Arc induction and new neuron integration into functional circuits in the injured hippocampi.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Neurogenesis and neuronal commitment following ischemia in a new mouse model for neonatal stroke.Brain Res. 2008 May 7;1208:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.037. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18387598 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of new neurons into functional neural networks.J Neurosci. 2006 Nov 22;26(47):12237-41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2195-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17122048 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic brain injury and behavioral impairments in a mouse model of term neonatal strokes.Behav Brain Res. 2009 Jan 30;197(1):77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.08.003. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Behav Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 18761039 Free PMC article.
-
Insult-induced aberrant hippocampal neurogenesis: Functional consequences and possible therapeutic strategies.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Oct 17;372:112032. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112032. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31199935 Review.
-
Hippocampal injury-induced cognitive and mood dysfunction, altered neurogenesis, and epilepsy: can early neural stem cell grafting intervention provide protection?Epilepsy Behav. 2014 Sep;38:117-24. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2013.12.001. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Epilepsy Behav. 2014. PMID: 24433836 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Shp2 in forebrain neurons regulates synaptic plasticity, locomotion, and memory formation in mice.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 May;35(9):1557-72. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01339-14. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25713104 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of trichostatin A and sodium valproate treatment on post-stroke neurogenesis and behavioral outcomes in immature mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Aug 19;7:123. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00123. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23966909 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep dysfunction following neonatal ischemic seizures are differential by neonatal age of insult as determined by qEEG in a mouse model.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Aug;116:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.04.012. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 29684437 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Circuit Activity during Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Seizures in Mice.Ann Neurol. 2019 Dec;86(6):927-938. doi: 10.1002/ana.25601. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Ann Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31509619 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic injection of CD34(+)-enriched human cord blood cells modulates poststroke neural and glial response in a sex-dependent manner in CD1 mice.Stem Cells Dev. 2015 Jan 1;24(1):51-66. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0135. Stem Cells Dev. 2015. PMID: 25121827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lynch JK, Hirtz DG, DeVeber G, Nelson KB. Report of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Workshop on Perinatal and Childhood Stroke. Pediatrics. 2002;109:116–123. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y, Holmes GL. Effects of seizures on developmental processes in the immature brain. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:1055–1063. - PubMed
-
- Hartel C, Schilling S, Sperner J, Thyen U. The clinical outcomes of neonatal and childhood stroke: review of the literature and implications for future research. Eur J Neurol. 2004;11:431–438. - PubMed
-
- Anderson V, Jacobs R, Spencer-Smith M, Coleman L, Anderson P, Williams J, et al. Does Early Age at Brain Insult Predict Worse Outcome? Neuropsychological Implications. J Pediatr Psychol. 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

