CD8+ T cell response in HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice is elicited by epitopes from SARS-CoV S protein
- PMID: 20709007
- PMCID: PMC7115361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.08.013
CD8+ T cell response in HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice is elicited by epitopes from SARS-CoV S protein
Abstract
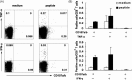
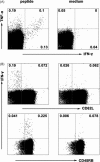
Cytotoxic CD8(+) T lymphocytes (CTLs) play an important role in antiviral immunity. Several human HLA-A*0201 restricted CTL epitopes of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) spike (S) protein have been identified in HLA-A*0201 transgenic (Tg) mice, but the mechanisms and properties of immune responses are still not well understood. In this study, HLA-A*0201 Tg mice were primed intramuscularly with SARS S DNA and boosted subcutaneously with HLA-A*0201 restricted peptides. The lymphocytes from draining lymph nodes, spleens and lungs were stimulated with the cognate peptides. Three different methods (ELISA, ELISPOT and FACS) were used to evaluate the immune responses during short and long periods of time after immunization. Results showed that peptide-specific CD8(+) T cells secreted IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-2 and expressed CD107a/b on cell surface. IFN-γ(+)CD8(+) T cells and CD107a/b(+)CD8(+) T cells distributed throughout the lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues, but the frequency of peptide-specific CD8(+) T cells was higher in lungs than in spleens and lymph nodes. The phenotype of the CD8(+) T cells was characterized based on the expression of IFN-γ. Most of the HLA-A*0201 restricted peptide-specific CD8(+) T cells represented a memory subset with CD45RB(high) and CD62L(low). Taken together, these data demonstrate that immunization with SARS S DNA and HLA-A*0201 restricted peptides can elicit antigen-specific CD8(+) T cell immune responses which may have a significant implication in the long-term protection. We provide novel information in cellular immune responses of SARS S antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells, which are important in the development of vaccine against SARS-CoV infection.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Priming with SARS CoV S DNA and boosting with SARS CoV S epitopes specific for CD4+ and CD8+ T cells promote cellular immune responses.Vaccine. 2007 Sep 28;25(39-40):6981-91. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.06.047. Epub 2007 Jul 16. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17709158 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-A*0201 T-cell epitopes in severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus nucleocapsid and spike proteins.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 May 26;344(1):63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.152. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16630549 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an HLA-A*0201-restricted CD8+ T-cell epitope SSp-1 of SARS-CoV spike protein.Blood. 2004 Jul 1;104(1):200-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-11-4072. Epub 2004 Mar 11. Blood. 2004. PMID: 15016646 Free PMC article.
-
SARS Immunity and Vaccination.Cell Mol Immunol. 2004 Jun;1(3):193-8. Cell Mol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 16219167 Review.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome: vaccine on the way.Chin Med J (Engl). 2005 Sep 5;118(17):1468-76. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005. PMID: 16157050 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A Murine CD8+ T Cell Epitope Identified in the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jun 11;9(6):641. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9060641. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34208032 Free PMC article.
-
The immune responses of HLA-A*0201 restricted SARS-CoV S peptide-specific CD8⁺ T cells are augmented in varying degrees by CpG ODN, PolyI:C and R848.Vaccine. 2011 Sep 2;29(38):6670-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.06.100. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21745520 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Identified HLA-A*0201-Restricted Hantaan Virus Glycoprotein Cytotoxic T-Cell Epitopes Could Effectively Induce Protective Responses in HLA-A2.1/Kb Transgenic Mice May Associate with the Severity of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2017 Dec 12;8:1797. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01797. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29312318 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Spike T-Cell Epitopes for Assessing T-Cell Immunity.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02002-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02002-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33443088 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell immunity of SARS-CoV: Implications for vaccine development against MERS-CoV.Antiviral Res. 2017 Jan;137:82-92. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Antiviral Res. 2017. PMID: 27840203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ksiazek T.G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C.S., Zaki S.R., Peret T., Emery S. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(20):1953–1966. - PubMed
-
- Drosten C., Gunther S., Preiser W., van der Werf S., Brodt H.R., Becker S. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(20):1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Normile D. Infectious diseases. Mounting lab accidents raise SARS fears. Science. 2004;304(5671):659–661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

