Generation of VSV pseudotypes using recombinant ΔG-VSV for studies on virus entry, identification of entry inhibitors, and immune responses to vaccines
- PMID: 20709108
- PMCID: PMC2956192
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2010.08.006
Generation of VSV pseudotypes using recombinant ΔG-VSV for studies on virus entry, identification of entry inhibitors, and immune responses to vaccines
Abstract
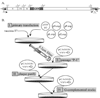
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is a prototypic enveloped animal virus that has been used extensively to study virus entry, replication and assembly due to its broad host range and robust replication properties in a wide variety of mammalian and insect cells. Studies on VSV assembly led to the creation of a recombinant VSV in which the glycoprotein (G) gene was deleted. This recombinant (rVSV-ΔG) has been used to produce VSV pseudotypes containing the envelope glycoproteins of heterologous viruses, including viruses that require high-level biocontainment; however, because the infectivity of rVSV-ΔG pseudotypes is restricted to a single round of replication the analysis can be performed using biosafety level 2 (BSL-2) containment. As such, rVSV-ΔG pseudotypes have facilitated the analysis of virus entry for numerous viral pathogens without the need for specialized containment facilities. The pseudotypes also provide a robust platform to screen libraries for entry inhibitors and to evaluate the neutralizing antibody responses following vaccination. This manuscript describes methods to produce and titer rVSV-ΔG pseudotypes. Procedures to generate rVSV-ΔG stocks and to quantify virus infectivity are also described. These protocols should allow any laboratory knowledgeable in general virological and cell culture techniques to produce successfully replication-restricted rVSV-ΔG pseudotypes for subsequent analysis.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abe K, Nozaki A, Tamura K, Ikeda M, Naka K, Dansako H, Hoshino HO, Tanaka K, Kato N. Tandem repeats of lactoferrin-derived anti-hepatitis C virus peptide enhance antiviral activity in cultured human hepatocytes. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007;51:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Fukushi S, Mizutani T, Saijo M, Matsuyama S, Miyajima N, Taguchi F, Itamura S, Kurane I, Morikawa S. Vesicular stomatitis virus pseudotyped with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2005;86:2269–2274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

