Molecular targets of apigenin in colorectal cancer cells: involvement of p21, NAG-1 and p53
- PMID: 20709524
- PMCID: PMC2988105
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.07.007
Molecular targets of apigenin in colorectal cancer cells: involvement of p21, NAG-1 and p53
Abstract
Persuasive epidemiological and experimental evidence suggests that dietary flavonoids have anti-cancer activity. Since conventional therapeutic and surgical approaches have not been able to fully control the incidence and outcome of most cancer types, including colorectal neoplasia, there is an urgent need to develop alternative approaches for the management of cancer. We sought to develop the best flavonoids for the inhibition of cell growth, and apigenin (flavone) proved to be the most promising compound in colorectal cancer cell growth arrest. Subsequently, we found that pro-apoptotic proteins (NAG-1 and p53) and cell cycle inhibitor (p21) were induced in the presence of apigenin, and kinase pathways, including PKCδ and ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM), play an important role in activating these proteins. The data generated by in vitro experiments were confirmed in an animal study using APC(MIN+) mice. Apigenin is able to reduce polyp numbers, accompanied by increasing p53 activation through phosphorylation in animal models. Our data suggest apparent beneficial effects of apigenin on colon cancer.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript
Figures

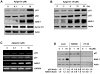
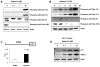



References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58(2):71–96. - PubMed
-
- Llorens F, Miró FA, Casañas A, Roher N, Garcia L, Plana M, et al. Unbalanced activation of ERK1/2 and MEK1/2 in apigenin-induced HeLa cell death. Experimental Cell Research. 2004;299(1):15–26. - PubMed
-
- Agullo G, Gamet-Payrastre L, Manenti S, Viala C, Rémésy C, Chap H, et al. Relationship between flavonoid structure and inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: A comparison with tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C inhibition. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1997;53(11):1649–1657. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Heideman L, Chung CS, Pelling JC, Koehler KJ, Birt DF. Cell-cycle arrest at G2/M and growth inhibition by apigenin in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Mol Carcinog. 2000;28(2):102–10. - PubMed
-
- Au A, Li B, Wang W, Roy H, Koehler K, Birt D. Effect of dietary apigenin on colonic ornithine decarboxylase activity, aberrant crypt foci formation, and tumorigenesis in different experimental models. Nutr Cancer. 2006;54(2):243–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

