High-molecular-weight hyaluronan is a novel inhibitor of pulmonary vascular leakiness
- PMID: 20709728
- PMCID: PMC2980391
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00405.2009
High-molecular-weight hyaluronan is a novel inhibitor of pulmonary vascular leakiness
Abstract
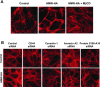
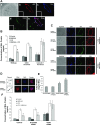
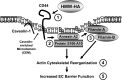
Endothelial cell (EC) barrier dysfunction results in increased vascular permeability, a perturbation observed in inflammatory states, tumor angiogenesis, atherosclerosis, and both sepsis and acute lung injury. Therefore, agents that enhance EC barrier integrity have important therapeutic implications. We observed that binding of high-molecular-weight hyaluronan (HMW-HA) to its cognate receptor CD44 within caveolin-enriched microdomains (CEM) enhances human pulmonary EC barrier function. Immunocytochemical analysis indicated that HMW-HA promotes redistribution of a significant population of CEM to areas of cell-cell contact. Quantitative proteomic analysis of CEM isolated from human EC demonstrated HMW-HA-mediated recruitment of cytoskeletal regulatory proteins (annexin A2, protein S100-A10, and filamin A/B). Inhibition of CEM formation [caveolin-1 small interfering RNA (siRNA) and cholesterol depletion] or silencing (siRNA) of CD44, annexin A2, protein S100-A10, or filamin A/B expression abolished HMW-HA-induced actin cytoskeletal reorganization and EC barrier enhancement. To confirm our in vitro results in an in vivo model of inflammatory lung injury with vascular hyperpermeability, we observed that the protective effects of HMW-HA on LPS-induced pulmonary vascular leakiness were blocked in caveolin-1 knockout mice. Furthermore, targeted inhibition of CD44 expression in the mouse pulmonary vasculature significantly reduced HMW-HA-mediated protection from LPS-induced hyperpermeability. These data suggest that HMW-HA, via CD44-mediated CEM signaling events, represents a potentially useful therapeutic agent for syndromes of increased vascular permeability.
Figures
References
-
- Balyasnikova IV, Sun ZL, Metzger R, Taylor PR, Vicini E, Muciaccia B, Visintine DJ, Berestetskaya YV, McDonald TD, Danilov SM. Monoclonal antibodies to native mouse angiotensin-converting enzyme (CD143): ACE expression quantification, lung endothelial cell targeting and gene delivery. Tissue Antigens 67: 10–29, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Bensadoun ES, Burke AK, Hogg JC, Roberts CR. Proteoglycan deposition in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154: 1819–1828, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Borbiev T, Verin AD, Shi S, Liu F, Garcia JG. Regulation of endothelial cell barrier function by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280: L983–L990, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Bourguignon LY, Gilad E, Brightman A, Diedrich F, Singleton P. Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with leukemia-associated RhoGEF and epidermal growth factor receptor promotes Rho/Ras co-activation, phospholipase Cε-Ca2+ signaling, and cytoskeleton modification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 281: 14026–14040, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Bourguignon LY, Ramez M, Gilad E, Singleton PA, Man MQ, Crumrine DA, Elias PM, Feingold KR. Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction stimulates keratinocyte differentiation, lamellar body formation/secretion, and permeability barrier homeostasis. J Invest Dermatol 126: 1356–1365, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

