Neutrophil elastase contributes to acute lung injury induced by bilateral nephrectomy
- PMID: 20709801
- PMCID: PMC2947264
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090793
Neutrophil elastase contributes to acute lung injury induced by bilateral nephrectomy
Abstract
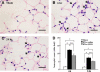
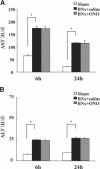
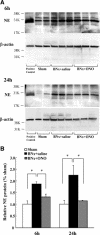
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a serious problem in critically ill patients of intensive care units. It has been reported previously that AKI can induce acute lung injury (ALI), as well as cause injuries to other remote organs, including the lungs. Patients with AKI complicated by ALI show remarkably high mortality. ALI is characterized by neutrophil infiltration into the lung. Neutrophil elastase (NE) is a key enzyme for tissue injury caused by activated neutrophils, such as occurs in ALI. Therefore, this study investigated the role of NE in AKI-induced ALI using a specific NE inhibitor, sivelestat sodium hydrate (ONO-5046), in a mouse bilateral nephrectomy model. Bilateral nephrectomy showed not only a remarkable increase in blood urea nitrogen levels, but also demonstrated neutrophil infiltration into the lung, increased pulmonary inflammatory cytokine expression [interleukin-6, neutrophil chemokine keratinocyte-derived chemokine, and tumor necrosis factor-α], and protein leakage with early increases in both systemic and pulmonary NE activity. ONO-5046 treatment reduced NE activity and improved these pulmonary inflammatory responses. Additionally, ONO-5046-treated animals had longer survival times. These data demonstrate that increasing NE activity induces pulmonary inflammatory damage in a bilateral nephrectomy model. Blockade of NE activity will be a useful therapeutic strategy for ALI complications in AKI patients.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Neutrophil elastase inhibitor (sivelestat) attenuates subsequent ventilator-induced lung injury in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Sep 24;571(1):62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.05.053. Epub 2007 Jun 9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17599828
-
Inhibition of neutrophil elastase contributes to attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury during neutropenia recovery in mice.J Anesth. 2017 Jun;31(3):397-404. doi: 10.1007/s00540-017-2311-9. Epub 2017 Jan 31. J Anesth. 2017. PMID: 28144780
-
Inhaled neutrophil elastase inhibitor reduces oleic acid-induced acute lung injury in rats.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Feb;25(1):99-103. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2011.12.006. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22210005
-
[Pharmacological profile of a specific neutrophil elastase inhibitor, Sivelestat sodium hydrate].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003 Aug;122(2):151-60. doi: 10.1254/fpj.122.151. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 12890901 Review. Japanese.
-
Neutrophil elastase inhibitor (sivelestat) may be a promising therapeutic option for management of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome or disseminated intravascular coagulation in COVID-19.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020 Dec;45(6):1515-1519. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13251. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020. PMID: 32860252 Review.
Cited by
-
Function of the p38MAPK-HSP27 pathway in rat lung injury induced by acute ischemic kidney injury.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:981235. doi: 10.1155/2013/981235. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23586067 Free PMC article.
-
The need for disruptive innovation in acute kidney injury.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2020 Nov;24(11):979-988. doi: 10.1007/s10157-020-01920-w. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32583160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between α1-Antitrypsin Deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Epidemiological Data and Pathogenetic Hypotheses.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 29;10(19):4493. doi: 10.3390/jcm10194493. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34640510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombospondin-1 restrains neutrophil granule serine protease function and regulates the innate immune response during Klebsiella pneumoniae infection.Mucosal Immunol. 2015 Jul;8(4):896-905. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.120. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Mucosal Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25492474 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of salivary markers of kidney functions in acute and chronic kidney diseases.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 4;10(1):21260. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78209-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33277585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chertow GM, Christiansen CL, Cleary PD, Munro C, Lazarus JM. Prognostic stratification in critically ill patients with acute renal failure requiring dialysis. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155:1505–1511. - PubMed
-
- Waikar SS, Liu KD, Chertow GM. Diagnosis, epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:844–861. - PubMed
-
- Scheel PJ, Liu M, Rabb H. Uremic lung: new insights into a forgotten condition. Kidney Int. 2008;74:849–851. - PubMed
-
- Faubel S. Pulmonary complications after acute kidney injury. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2008;15:284–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

