Metastasis-associated protein 1 short form stimulates Wnt1 pathway in mammary epithelial and cancer cells
- PMID: 20710043
- PMCID: PMC3617568
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0907
Metastasis-associated protein 1 short form stimulates Wnt1 pathway in mammary epithelial and cancer cells
Abstract
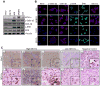
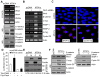
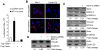
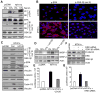
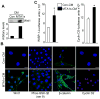
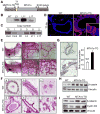
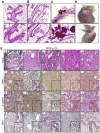
Although Wnt1 downstream signaling components as well as cytoplasmic level of metastatic tumor antigen 1 short form (MTA1s) are elevated in human breast cancer, it remains unknown whether a regulatory cross-talk exists between these two pathways. Here, we provide evidence of a remarkable correlation between the levels of MTA1s and stimulation of the Wnt1 signaling components, leading to increased stabilization of beta-catenin and stimulation of Wnt1 target genes in the murine mammary epithelial and human breast cancer cells. We found that MTA1s influences Wnt1 pathway through extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling as selective silencing of the endogenous MTA1s or ERK, or its target glycogen synthase kinase 3beta resulted in a substantial decrease in beta-catenin expression, leading to the inhibition of Wnt1 target genes. Furthermore, downregulation of beta-catenin in cells with elevated MTA1s level was accompanied by a corresponding decrease in the expression of Wnt1 target genes, establishing a mechanistic role for the ERK/glycogen synthase kinase 3beta/beta-catenin pathway in the stimulation of the Wnt1 target genes by MTA1s in mammary epithelial cells. In addition, mammary glands from the virgin MTA1s transgenic mice mimicked the phenotypic changes found in the Wnt1 transgenic mice and exhibited an overall hyperactivation of the Wnt1 signaling pathway, leading to increased stabilization and nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin. Mammary glands from the virgin MTA1s-TG mice revealed ductal hyperplasia and ductal carcinoma in situ, and low incidence of palpable tumors. These findings reveal a previously unrecognized role for MTA1s as an important modifier of the Wnt1 signaling in mammary epithelial and cancer cells.
(c)2010 AACR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metastasis-associated protein 1 and its short form variant stimulates Wnt1 transcription through promoting its derepression from Six3 corepressor.Cancer Res. 2010 Aug 15;70(16):6649-58. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0909. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20682799 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells requires β-catenin activation via Akt/GSK3- and MTA1/Wnt1 protein-dependent pathways.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):8598-612. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.322800. Epub 2012 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22270359 Free PMC article.
-
Twist is up-regulated in response to Wnt1 and inhibits mouse mammary cell differentiation.Cancer Res. 2003 Apr 15;63(8):1906-13. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12702582
-
MTA family of transcriptional metaregulators in mammary gland morphogenesis and breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007 Sep;12(2-3):115-25. doi: 10.1007/s10911-007-9043-7. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007. PMID: 17549610 Review.
-
New steps in the Wnt/beta-catenin signal transduction pathway.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000;55:225-36. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000. PMID: 11036939 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of MTA1 in cancer progression and metastasis.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014 Dec;33(4):879-89. doi: 10.1007/s10555-014-9515-3. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014. PMID: 25344802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MTA1 overexpression induces cisplatin resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by promoting cancer stem cells properties.Mol Cells. 2014 Sep;37(9):699-704. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2014.0029. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Mol Cells. 2014. PMID: 25245523 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis-associated protein 1/nucleosome remodeling and histone deacetylase complex in cancer.Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 15;72(2):387-94. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2345. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22253283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MTA1 promotes STAT3 transcription and pulmonary metastasis in breast cancer.Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 15;73(12):3761-70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3998. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23580571 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of MTA1 protein overexpression-linked invasion: MTA1 regulation of hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (HMMR) expression and function.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 17;287(8):5483-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.324632. Epub 2011 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2012. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 6;288(36):26177. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A111.324632. PMID: 22203674 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127(3):469–80. - PubMed
-
- Karim R, Tse G, Putti T, Scolyer R, Lee S. The significance of the wnt pathway in the pathology of human cancers. Pathology. 2004;36(2):120–8. - PubMed
-
- Tsukamoto AS, Grosschedl R, Guzman RC, Parslow T, Varmus HE. Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell. 1988;55(4):619–25. - PubMed
-
- Eastman Q, Grosschedl R. Regulation of LEF-1/TCF transcription factors by wnt and other signals. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11(2):233–40. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, et al. Control of beta-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell. 2002;108(6):837–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

