Common genetic variation in the HLA region is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 20711177
- PMCID: PMC2930111
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.642
Common genetic variation in the HLA region is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson's disease
Abstract
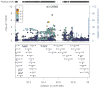
Parkinson's disease is a common disorder that leads to motor and cognitive disability. We performed a genome-wide association study of 2,000 individuals with Parkinson's disease (cases) and 1,986 unaffected controls from the NeuroGenetics Research Consortium (NGRC). We confirmed associations with SNCA and MAPT, replicated an association with GAK (using data from the NGRC and a previous study, P = 3.2 x 10(-9)) and detected a new association with the HLA region (using data from the NGRC only, P = 2.9 x 10(-8)), which replicated in two datasets (meta-analysis P = 1.9 x 10(-10)). The HLA association was uniform across all genetic and environmental risk strata and was strong in sporadic (P = 5.5 x 10(-10)) and late-onset (P = 2.4 x 10(-8)) disease. The association peak we found was at rs3129882, a noncoding variant in HLA-DRA. Two studies have previously suggested that rs3129882 influences expression of HLA-DR and HLA-DQ. The brains of individuals with Parkinson's disease show upregulation of DR antigens and the presence of DR-positive reactive microglia, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs reduce Parkinson's disease risk. The genetic association with HLA supports the involvement of the immune system in Parkinson's disease and offers new targets for drug development.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Payami H, Larsen K, Bernard S, Nutt J. Increased risk of Parkinson’s disease in parents and siblings of patients. Ann Neurol. 1994;36:659–661. - PubMed
-
- Kay DM, et al. Genetic association between alpha-synuclein and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2008;147B:1222–30. - PubMed
-
- Powers K, et al. Combined effects of smoking, coffee and NSAIDs on Parkinson’s disease risk. Mov Disord. 2008;23:88–95. - PubMed
-
- McCulloch CC, et al. Exploring gene-environment interactions in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Genet. 2008;123:257–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30AG08017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS36960/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS039764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036960/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG027944/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027944/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS039764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH087336/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21MH087336/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000531/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

