Natural killer cell-triggered vascular transformation: maternal care before birth?
- PMID: 20711229
- PMCID: PMC3079746
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2010.38
Natural killer cell-triggered vascular transformation: maternal care before birth?
Abstract
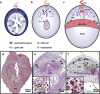
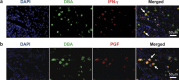
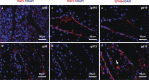
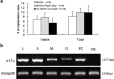
Natural killer (NK) cells are found in lymphoid and non-lymphoid organs. In addition to important roles in immune surveillance, some NK cells contribute to angiogenesis and circulatory regulation. The uterus of early pregnancy is a non-lymphoid organ enriched in NK cells that are specifically recruited to placental attachment sites. In species with invasive hemochorial placentation, these uterine natural killer (uNK) cells, via secretion of cytokines, chemokines, mucins, enzymes and angiogenic growth factors, contribute to the physiological change of mesometrial endometrium into the unique stromal environment called decidua basalis. In humans, uNK cells have the phenotype CD56(bright)CD16(dim) and they appear in great abundance in the late secretory phase of the menstrual cycle and early pregnancy. Gene expression studies indicate that CD56(bright)CD16(dim) uterine and circulating cells are functionally distinct. In humans but not mice or other species with post-implantation decidualization, uNK cells may contribute to blastocyst implantation and are of interest as therapeutic targets in female infertility. Histological and genetic studies in mice first identified triggering of the process of gestation spiral arterial modification as a major uNK cell function, achieved via interferon (IFN)-γ secretion. During spiral arterial modification, branches from the uterine artery that traverse the endometrium/decidua transiently lose their muscular coat and ability to vasoconstrict. The expression of vascular markers changes from arterial to venous as these vessels dilate and become low-resistance, high-volume channels. Full understanding of the vascular interactions of human uNK cells is difficult to obtain because endometrial time-course studies are not possible in pregnant women. Here we briefly review key information concerning uNK cell functions from studies in rodents, summarize highlights concerning human uNK cells and describe our preliminary studies on development of a humanized, pregnant mouse model for in vivo investigations of human uNK cell functions.
Figures
References
-
- Peel S. Granulated metrial gland cells. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1989;115:1–112. - PubMed
-
- Manaster I, Mizrahi S, Goldman-Wohl D, Sela HY, Stern-Ginossar N, Lankry D, et al. Endometrial NK cells are special immature cells that await pregnancy. J Immunol. 2008;181:1869–1876. - PubMed
-
- Lash GE, Robson SC, Bulmer JN. Review: functional role of uterine natural killer (uNK) cells in human early pregnancy decidua. Placenta. 2010;31:S87–S92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

