A Rac-Pak signaling pathway is essential for ErbB2-mediated transformation of human breast epithelial cancer cells
- PMID: 20711231
- PMCID: PMC2965784
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.318
A Rac-Pak signaling pathway is essential for ErbB2-mediated transformation of human breast epithelial cancer cells
Abstract
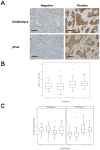
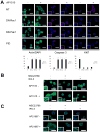
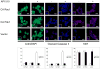
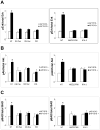
The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases, particularly ErbB2, has an important role in the genesis of breast cancer. ErbB2 kinase activity promotes Ras-mediated stimulation of downstream protein kinase cascades, including the Ras/Raf-1/MAPK/ERK kinase (Mek)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) pathway, leading to tumor cell growth and migration. Signaling through the Ras-Erk pathway can be influenced by p21-activated kinase-1 (Pak1), an effector of the Rho family GTPases Rac and Cdc42. In this study, we asked if ErbB2 expression correlates with Pak1 and Erk activity in human breast cancer specimens, and if Pak1 signaling is required for ErbB2 transformation in a three-dimensional (3D) in vitro setting and in xenografts. We found a correlation between ErbB2 expression and activation of Pak in estrogen receptor-positive human breast tumor samples and observed that in 3D cultures, activation of Rac-Pak1 pathway by ErbB2 homodimers induced growth factor-independent proliferation and promoted disruption of 3D mammary acinar-like structures through activation of the Erk and Akt pathways. Further, we found that inhibition of Pak1 by small molecules compromised activation of Erk and Akt, resulting in reversion of the malignant phenotype and restoration of normal acinar architecture. Finally, ErbB2-amplified breast cancer cells expressing a specific Pak inhibitor showed delayed tumor formation and downregulation of Erk and Akt signaling in vivo. These data imply that the Rac-Pak pathway is vital to ErbB2-mediated transformation and that Pak inhibitors represent plausible drug targets in breast cancers in which ErbB2 signaling is activated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Amundadottir LT, Leder P. Oncogene. 1998;16:737–746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

