Human embryonic and rat adult stem cells with primitive endoderm-like phenotype can be fated to definitive endoderm, and finally hepatocyte-like cells
- PMID: 20711405
- PMCID: PMC2920330
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012101
Human embryonic and rat adult stem cells with primitive endoderm-like phenotype can be fated to definitive endoderm, and finally hepatocyte-like cells
Abstract
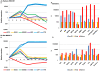
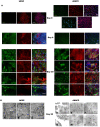
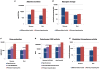
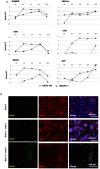
Stem cell-derived hepatocytes may be an alternative cell source to treat liver diseases or to be used for pharmacological purposes. We developed a protocol that mimics mammalian liver development, to differentiate cells with pluripotent characteristics to hepatocyte-like cells. The protocol supports the stepwise differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (ESC) to cells with characteristics of primitive streak (PS)/mesendoderm (ME)/definitive endoderm (DE), hepatoblasts, and finally cells with phenotypic and functional characteristics of hepatocytes. Remarkably, the same protocol can also differentiate rat multipotent adult progenitor cells (rMAPCs) to hepatocyte-like cells, even though rMAPC are isolated clonally from cultured rat bone marrow (BM) and have characteristics of primitive endoderm cells. A fraction of rMAPCs can be fated to cells expressing genes consistent with a PS/ME/DE phenotype, preceding the acquisition of phenotypic and functional characteristics of hepatocytes. Although the hepatocyte-like progeny derived from both cell types is mixed, between 10-20% of cells are developmentally consistent with late fetal hepatocytes that have attained synthetic, storage and detoxifying functions near those of adult hepatocytes. This differentiation protocol will be useful for generating hepatocyte-like cells from rodent and human stem cells, and to gain insight into the early stages of liver development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differentiation of rat multipotent adult progenitor cells to functional hepatocyte-like cells by mimicking embryonic liver development.Nat Protoc. 2010 Jul;5(7):1324-36. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2010.80. Epub 2010 Jun 24. Nat Protoc. 2010. PMID: 20595960
-
Transcriptional profiling of human embryonic stem cells differentiating to definitive and primitive endoderm and further toward the hepatic lineage.Stem Cells Dev. 2010 Jul;19(7):961-78. doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0220. Stem Cells Dev. 2010. PMID: 19757991
-
Derivation of high-purity definitive endoderm from human parthenogenetic stem cells using an in vitro analog of the primitive streak.Cell Transplant. 2012;21(1):217-34. doi: 10.3727/096368911X582723. Epub 2011 Jun 9. Cell Transplant. 2012. PMID: 21669044
-
Embryonic stem cells: hepatic differentiation and regenerative medicine for the treatment of liver disease.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2006 May;1(2):139-56. doi: 10.2174/157488806776956878. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 18220863 Review.
-
[Robust differentiation of fetal hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells and iPS].Med Sci (Paris). 2010 Dec;26(12):1061-6. doi: 10.1051/medsci/201026121061. Med Sci (Paris). 2010. PMID: 21187045 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Culture of mouse amniotic fluid-derived cells on irradiated STO feeders results in the generation of primitive endoderm cell lines capable of self-renewal in vitro.Cells Tissues Organs. 2013;198(2):111-26. doi: 10.1159/000353942. Epub 2013 Sep 21. Cells Tissues Organs. 2013. PMID: 24060676 Free PMC article.
-
Human Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial-Hepatic Platform for Efficacy Testing of Vascular-Protective Metabolites from Nutraceuticals.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Mar;6(3):851-863. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0129. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28297582 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-specific hepatocyte-like cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells model pazopanib-mediated hepatotoxicity.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 25;7:41238. doi: 10.1038/srep41238. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28120901 Free PMC article.
-
Spheroid culture for enhanced differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to hepatocyte-like cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2014 Jan 15;23(2):124-31. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0097. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Stem Cells Dev. 2014. PMID: 24020366 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells and multipotent adult progenitor cells.Immunol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;91(1):32-9. doi: 10.1038/icb.2012.64. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23295415 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gómez-Lechón MJ, Castell JV, Donato MT. An update on metabolism studies using human hepatocytes in primary culture. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2008;4:837–854. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura M, Koeda A, Suganuma Y, Suzuki E, Shimizu T, et al. Comparison of inducibility of CYP1A and CYP3A mRNAs by prototypical inducers in primary cultures of human, cynomolgus monkey, and rat hepatocytes. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2007;22:178–186. - PubMed
-
- Dhawan A, Mitry RR, Hughes RD. Hepatocyte transplantation for liver-based metabolic disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2006;29:431–435. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RA, Strom SC. Human Hepatocyte Transplantation: Worldwide Results. Transplantation. 2006;82:441–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

